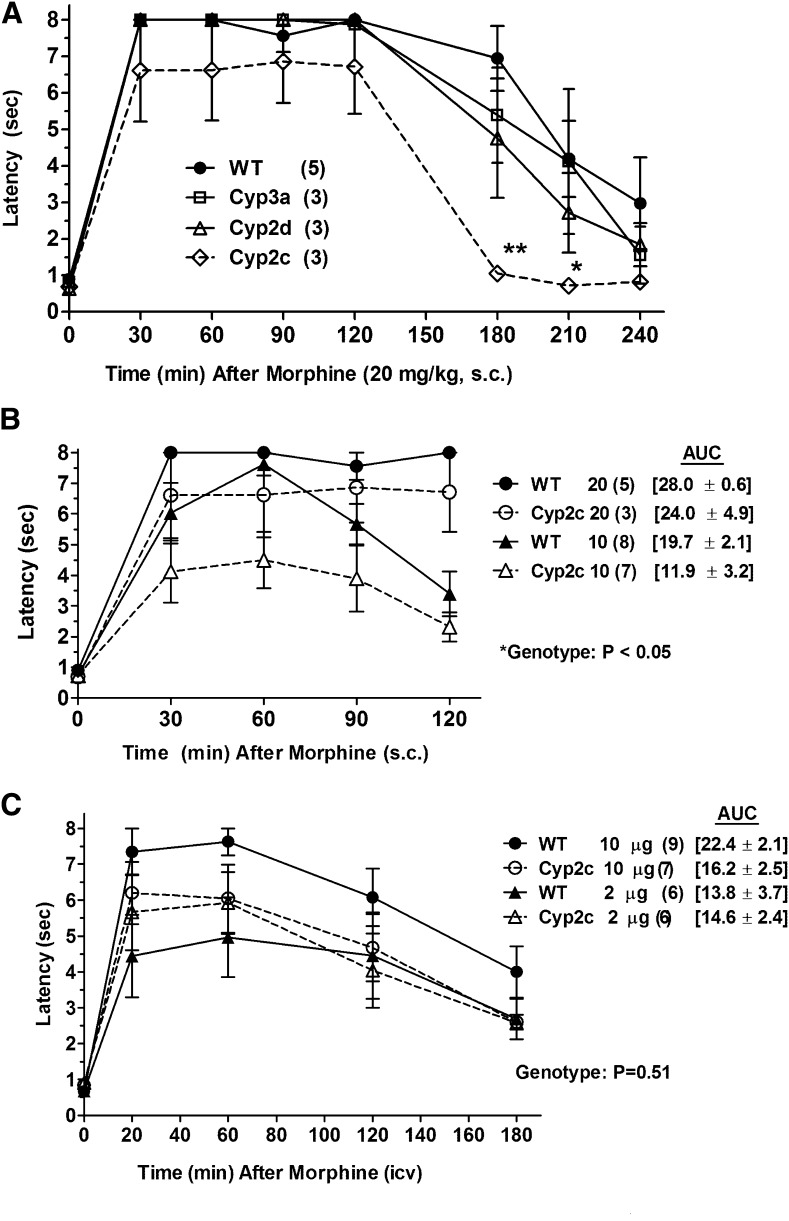
Fig. 1.
Morphine antinociception in P450 KO mice. (A) Control (WT) and three lines of P450 gene cluster KO mice were baseline tested for nociceptive latencies (zero time), received morphine sulfate (20 mg/kg, s.c.), and were retested at the indicated postinjection times [abscissa (minutes)]. Nociceptive latencies (sec, mean ± S.E.M., ordinate) are shown for the number of subjects designated in parentheses (*P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01, respectively) versus WT at the same time. (B) Morphine antinociception in WT and Cyp2c KO mice, shown as in (A), after two doses of morphine (10 and 20 mg/kg, s.c.). Data from the 20 mg/kg group are redrawn from (A). The AUCs (mean ± S.E.M., sec, 30–120 minutes) are given in brackets for the four groups. The *ANOVA of latencies found a significant main effect (P < 0.05) of genotype. (C) WT and Cyp2c KO mice were baseline tested (zero time), received the indicated dose of morphine sulfate (i.c.v.), and were retested at the designated postinjection times [abscissa (minutes)]. Latencies (sec, mean ± S.E.M., ordinate) are shown for the number of subjects in parentheses. The AUCs are given in brackets (mean ± S.E.M., sec, 20–180 minutes) for the four groups. No genotype differences were detected after i.c.v. morphine.