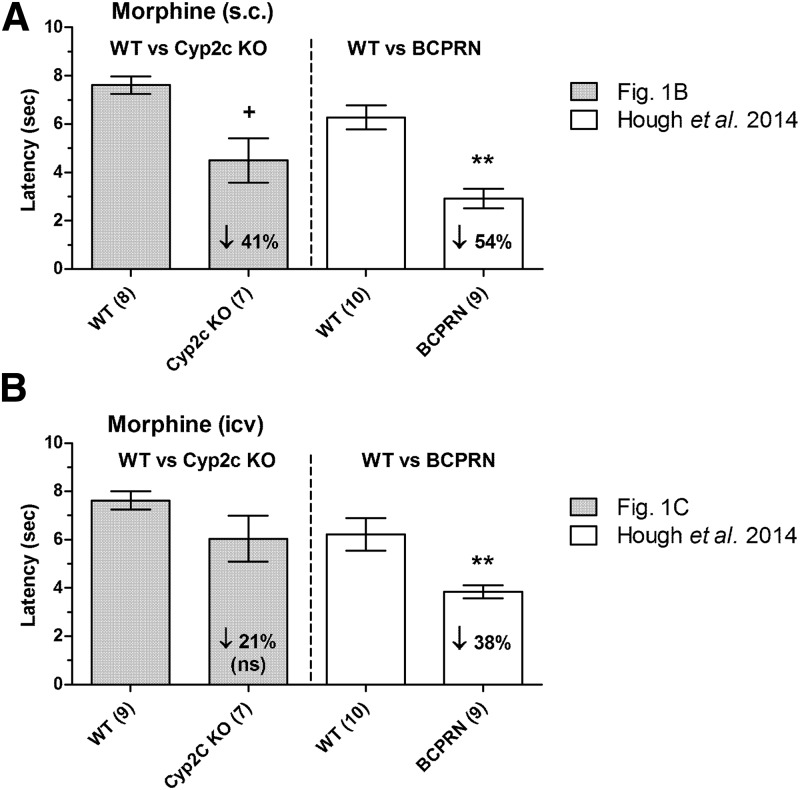
Fig. 2.
Deficits in morphine analgesia in two genotypes of P450-deficient mice. Responses in Cyp2c KO mice are compared with those found in BCPRN mice, a conditional KO lacking microsomal brain neuronal P450 activity. Latencies (ordinates, mean ± S.E.M.) are shown for each treatment of the number of subjects in parentheses. (A) Effects of s.c.-administered morphine in Cyp2c KO and WT control mice (two left-hand-side bars, data are 60 minutes after 10 mg/kg, s.c.; data from Fig. 1B) versus BCPRN and WT mice [two right-hand-side bars, data are 90 minutes after 20 mg/kg, s.c.; data from Hough et al. (2014)]. (B) Effects of i.c.v.-administered morphine (60 minutes after 10 µg) in Cyp2c KO and WT control mice (two left-hand-side bars; data from Fig. 1C) and in BCPRN and WT mice [two right-hand-side bars; data from Hough et al. (2014)]. Downward arrows show mean percent reductions in responses in each mutant genotype versus respective WT controls. **BCPRN, responses significantly different (P < 0.01) versus WT by ANOVA and post hoc comparisons. +Significant (P < 0.05) genotype difference revealed by ANOVA, but not significantly different at this time by post hoc testing.