Figure 5.
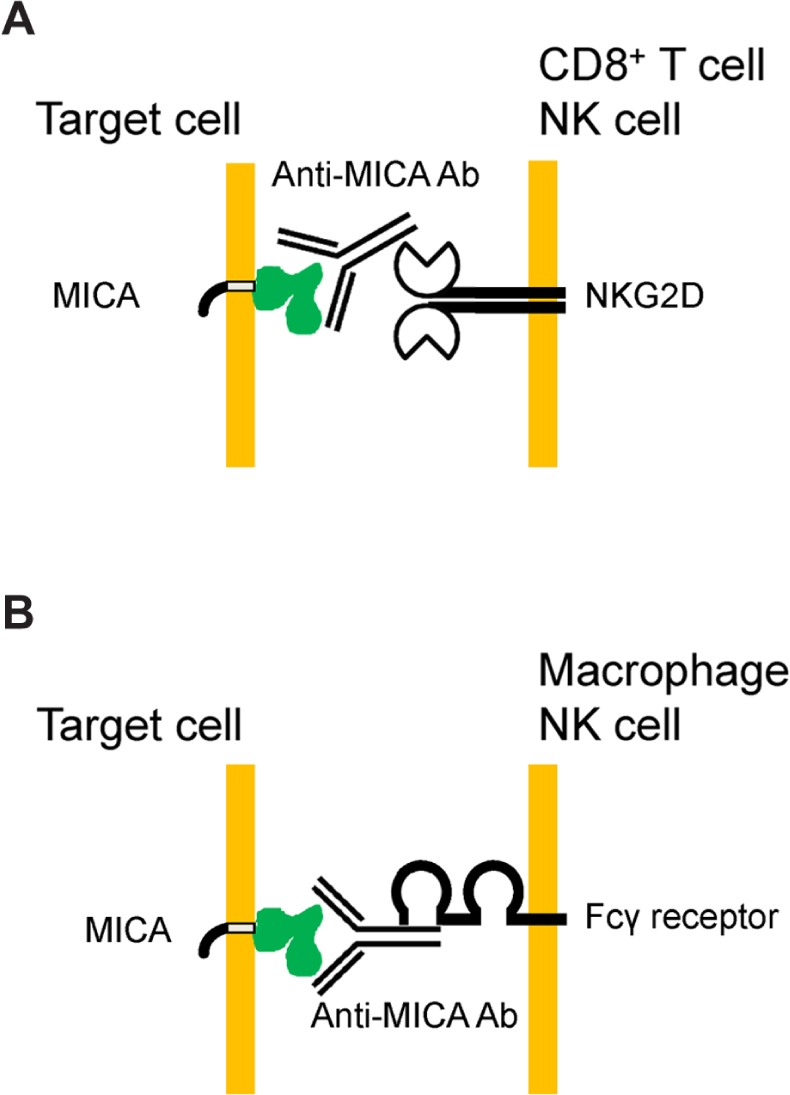
Hypotheses on the roles of anti-MICA Abs. (A) Anti-MICA Abs block the NKG2D–MICA interaction and prevent the stimulation of CD8+ T cells or NK cells for clearance of microorganisms, causing sustained inflammation followed by the fibrotic changes of the lung. (b) Chronically produced auto-Abs for MICA in RA patients may cause injury of the pulmonary epithelial cells expressing MICA by antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity.
