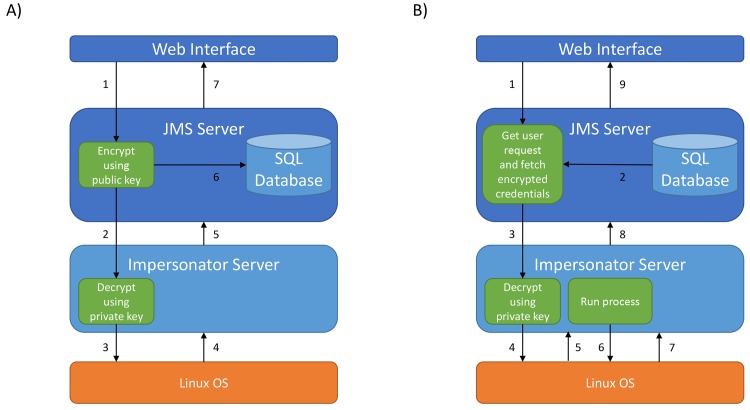
Fig 11. Impersonator Server.
A) The login process– 1) credentials are received from the web interface and encrypted using the public key. 2) Encrypted credentials are sent to the Impersonator server where they are decrypted using the private key. 3) Decrypted credentials are used to authenticate the user. 4) The OS responds to the authentication request. 5) The Impersonator server returns the response to the JMS server. 6) If successfully authenticated, the encrypted credentials on the JMS side are stored in the database. 7) The user is redirected to the JMS home page. B) Executing a command– 1) Request is sent from interface. 2) Encrypted credentials are fetched from database. 3) Based on the user request, a command is formulated and sent to the Impersonator server along with the encrypted credentials. 4) The Impersonator server decrypts the credentials and attempts to authenticate the user. 5) The OS responds to the authentication request. 6) A process is spawned in the users name and the command is run. 7) Output from the command is returned. 8) Output from the command is transferred back to the JMS server, which parse is and acts accordingly. 9) A response is sent to the user.