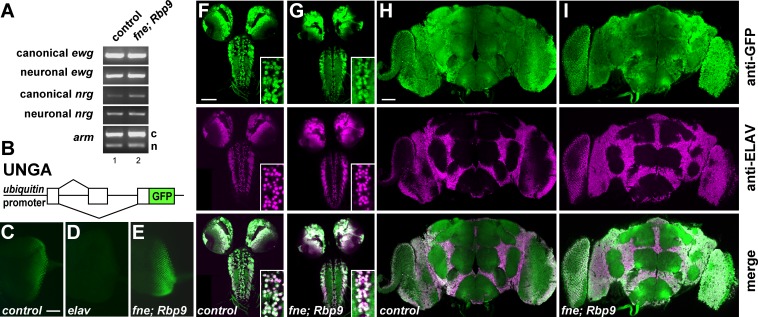
FIG 2.
Loss of FNE and RBP9 does not affect alternative splicing of ELAV target genes erect wing, neuroglian, and armadillo. (A) Analysis of neuronal alternative splicing in the ewg, nrg, and arm genes in fne; Rbp9 double mutants by RT-PCR. n, neuronal isoform; c, canonical isoform. (B) Schematic of the ELAV-responsive nrg GFP reporter UNGA. (C to E) Alternative splicing of nrg from the UNGA reporter, visualized by anti-GFP staining, is not affected in photoreceptor neurons of fne; Rbp9 mutants but is dramatically reduced in elavedr mutants. Scale bar, 50 μm. (F to I) Alternative splicing of nrg from the UNGA reporter is not affected in neurons of the third-instar larval or adult brain in fne; Rbp9 mutants, which were visualized with anti-GFP staining (top row) and in comparison to anti-ELAV staining (middle and bottom rows). Note the complete overlap between ELAV expression and GFP from the spliced UNGA reporter in fne; Rbp9 mutants (bottom rows of panels F to I). Scale bar, 100 μm.