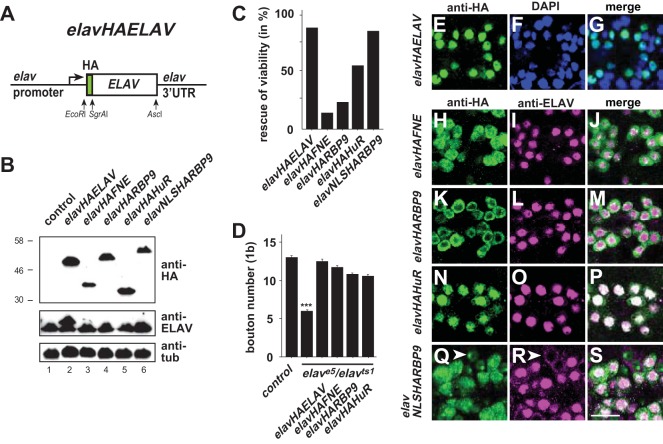
FIG 6.
FNE, RBP9, and HuR can replace neuronal ELAV function under the control of the elav gene. (A) Schematic of the elav rescue construct elav-HA-ELAV. (B) Expression of HA-tagged ELAV (e.g., HAELAV), FNE, RBP9, and HuR under the control of the elav gene in adult flies was determined by Western blotting detection with anti-HA antibodies. In lane 2, HA-tagged ELAV has a larger size due to the presence of the HA tag. (C) Rescue of adult viability of strong hypomorph elavts1 by expression of HA-tagged ELAV, FNE, RBP9, HuR, and NLSRBP9 under the control of the elav gene (n = 200 to 400). (D) Rescue of synaptic growth in elave5/elavts1 flies (raised at the permissive temperature during embryonic development) by expression of HA-tagged ELAV, FNE, RBP9, and HuR under the control of the elav gene is shown as the mean plus standard error of the mean of the number of type 1b boutons at muscle 13 (n = 15 to 28). (E to S) Cellular localization of HA-tagged ELAV, FNE, RBP9, HuR, and NLSRBP9 under the control of the elav gene in larval ventral nerve cord midline neurons. Staining with anti-HA, DAPI, and anti-ELAV is as indicated at the top of the panels. Arrowheads point toward neurons, where NLSHARBP9 is predominantly nuclear, while ELAV becomes cytoplasmic. Scale bar, 10 μm.