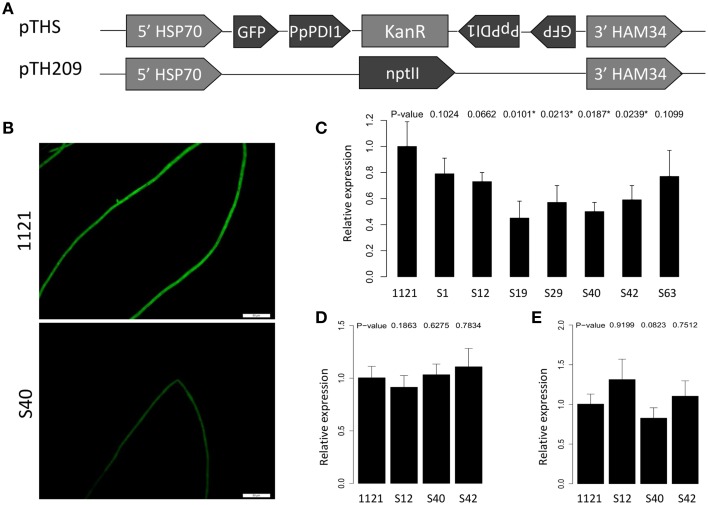
Figure 4.
Generation and analysis of PpPDI1-silencing P. parasitica transformants. (A) Constructs used for silencing in P. parasitica transformant 1121 that stably expresses GFP. In all constructs, transgenes are driven by the constitutive Bremia lactuca HSP70 promotor and HAM34 terminator. Plasmid pTHS contains 291 bp of PpPDI1 and 319 bp of GFP in the sense and antisense orientations separated by the linker sequence [kanamycin-resistant gene (kanR)]. Plasmid TH209 contains the nptII gene and was used as the selection marker in the co-transformation of P. parasitica. (B) Hyphae of PpPDI1-silencing transformants (S40), showing significantly reduced GFP signal compared with the recipient transformant 1121 (bar, 50 μm). (C) Expression analysis of PpPDI1 in the transformants with reduced GFP signals. Real-time RT-PCR evaluation of PpPDI1 expression used hyphal RNA from the recipient transformant 1121 and seven transformants with significantly reduced GFP signals. Three transformants (S12, S40, and S42) were selected for further characterization. (D) Expression analysis of PpPDI1 in P. parasitica 1121 and three transformants (S12, S40, and S42) during infection of N. benthamiana. Real-time RT-PCR evaluation of PpPDI1 expression used hyphal RNA from the infection tissues 60 hpi. (E) Expression analysis of PpPDI1 in P. parasitica 1121 and three transformants (S12, S40, and S42) subcultured for 3 weeks. Real-time RT-PCR evaluation of PpPDI1 expression used hyphal RNA from the vegetative hyphae. All the real-time RT-PCR experiments were repeated three times with independent RNA isolations. Bars represent the standard errors of three biological replicates. P. parasitica WS041 was used as a reference gene for quantification and normalization of PpPDI1 expression.