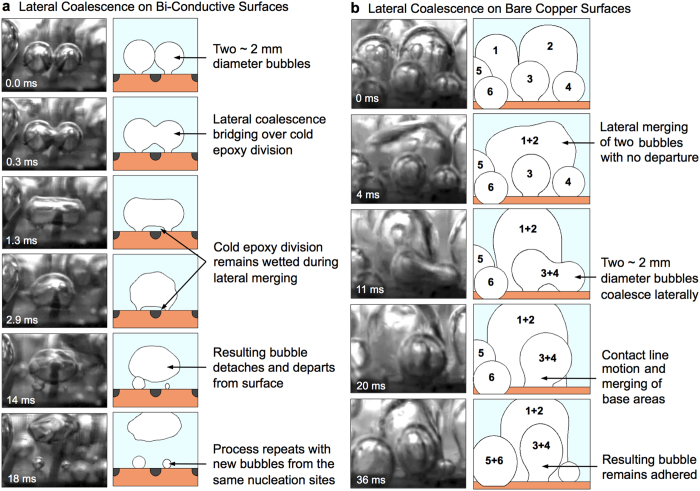
Figure 4. Lateral coalescence, contact line motion, and bubble departure.
High-speed time lapse imaging of the lateral coalescence of attached vapor bubbles on (a) bi-conductive surfaces, and (b) bare copper surfaces at ~10–15 W/cm2. (a) When two bubbles laterally coalesce over an epoxy division, the cold epoxy remains wetted and no contact line motion is observed. By remaining wetted at all times, the epoxy divisions promote departure at small diameters and maintain ordered flow paths for replenishing liquid. (b) Conversely, lateral coalescence on bare copper surfaces typically includes the lateral motion of contact lines, and merging of non-wetted base areas beneath the vapor bubbles.