Fig. 2.
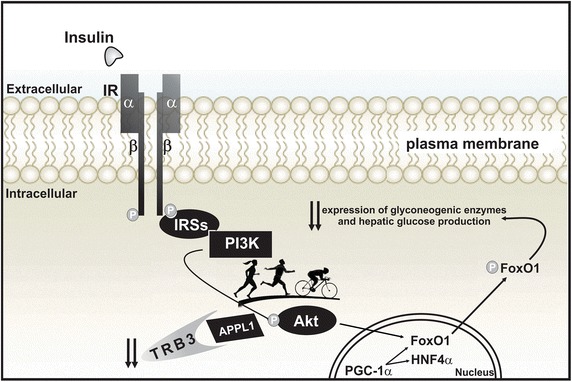
On the other hand, exercise markedly increases the expression of APPL1 and reduces the expression of TRB3, increasing hepatic insulin sensitivity and leading to the reduction of hyperglycemia due to a higher Akt phosphorylation. The activation of Akt allows the propagation of the insulin signal and the phosphorylation of Foxo1, which will exit the nucleus to the cytoplasm to decrease hepatic glucose production. These new findings allow us to better understand the molecular effects of physical exercise on the liver and its favorable effect on glycemic control and diabetes
