Fig. 5.
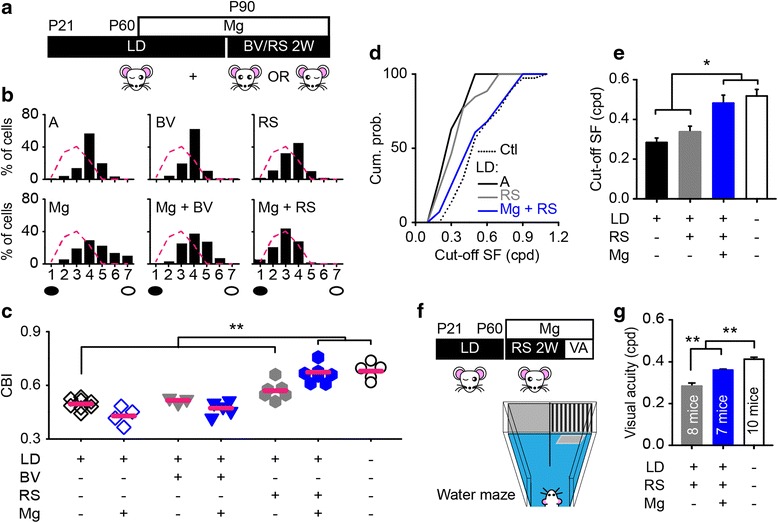
Magnesium facilitates the recovery of visual functions in adult amblyopic mice. a Schematic of the experimental procedure. 2 weeks of RS or BV were proceeded by 1 month of magnesium treatment in adult amblyopic mice. LD, long-term MD. b Comparison of the OD distribution in amblyopic group (A; CBI = 0.50 ± 0.01, 166 cells in 8 mice), amblyopic group with binocular vision (BV; CBI = 0.52 ± 0.01, 66 cells in 3 mice), reverse suturing (RS; CBI = 0.57 ± 0.02, 118 cells in 6 mice) or chronic magnesium treatment (Mg; CBI = 0.43 ± 0.03, 89 cells in 4 mice), and magnesium-treated amblyopic groups with binocular vision (Mg + BV; CBI = 0.7 ± 0.02, 99 cells in 5 mice) or reverse suturing (Mg + RS; CBI = 0.67 ± 0.02, 168 cells in 8 mice). The red dashed curve represents the OD distribution of normal adult mice shown in (Fig. 1b). Filled black circles represent the eye with LD, and open black circles represent the fellow eye. c Summary of the CBI values in each group. The horizontal bar represents the mean value. Each symbol represents one animal. d, e The cumulative distributions (d) and mean values (e) of the cut-off spatial frequency (cut-off SF) of V1b neurons driven by long-term deprived eye in amblyopic (27 neurons, 8 mice), reverse sutured amblyopic (26 neurons, 8 mice), magnesium-treated reverse sutured amblyopic (28 neurons, 8 mice) group, and either eye in control group (Ctl; 37 neurons, 5 mice). A and RS versus Ctl and Mg + RS, P < 0.01 using Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. f Schematic of the experimental procedure and the two-alternative forced-choice discrimination task. Visual acuity (VA) was measured following 2 weeks of magnesium treatment and RS. g Behavioral VA of the eye with LD in amblyopic mice and either eye in control mice. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 using a one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. Error bars, SEM
