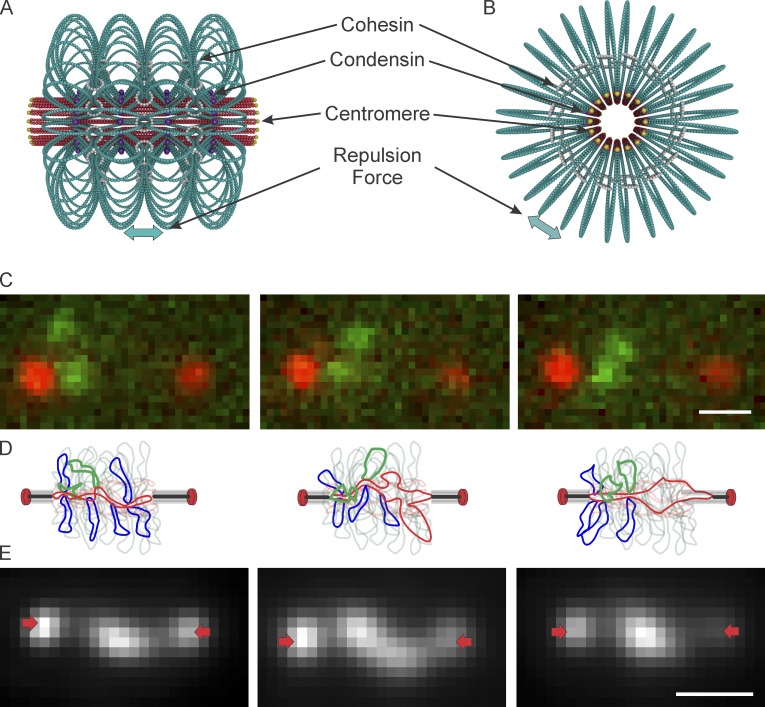
Figure 6.
Mechanistic basis for extensional forces from packed centromere DNA loops. (A) Model of pericentric chromatin in budding yeast. The pericentric chromatin from all 16 chromosomes is shown. 50 kb of DNA (red and teal) surround the centromeres, shown at the apex of a DNA loop (centromere DNA in yellow, DNA primary axis in red) and form a cylinder around the spindle microtubules (not depicted). Sister centromeres are at opposite ends of the cylinder. DNA loops (teal) are formed via the action of condensin (purple) binding to the base of loops. The number of loops and their geometric arrangement are based on experimental evidence from the spatial segregation of condensin, cohesin, and LacO DNA arrays. The loops repel each other, resulting in a net outward/poleward force. Cohesin rings are depicted in white. (B) End-on view of the model. (C) Time-lapse of pericentric LacO arrays in cbf5-AUU mutant yeast during metaphase. (D) Schematic of sister chromatid loop fluctuations (in green) over time. SPBs (red ovals), lines are kMTs. Chromatin proximal to the spindle axis is indicated as the red line, loops extending off axis are indicated in blue. The green loops depict the labeled chromatin in C. Microtubule shortening will release condensin bound at the base of a loop as the DNA transits from a radial to an axial position (panels should be read left to right). The release of a loop results in a precipitous drop in tension as a result of increased DNA length along the axis. As the microtubule shortens, DNA (red) elongates along the spindle axis, until it reaches equilibrium and greater force is required to further stretch the fiber. This leads to tension-dependent microtubule rescue, allowing the DNA to recoil and adopt a random coil. DNA fluctuation off the spindle axis allows condensin binding and loop formation (panels should be read right to left). (E) Time-lapse of TetO/TetR-GFP labeled, dicentric plasmid. These plasmids lie along the primary axis, where tension force is sufficient to extend the chromatin beyond its nucleosomal length. SPBs are indicated with arrows (red). Bar, 0.5 µm.