Figure 1.
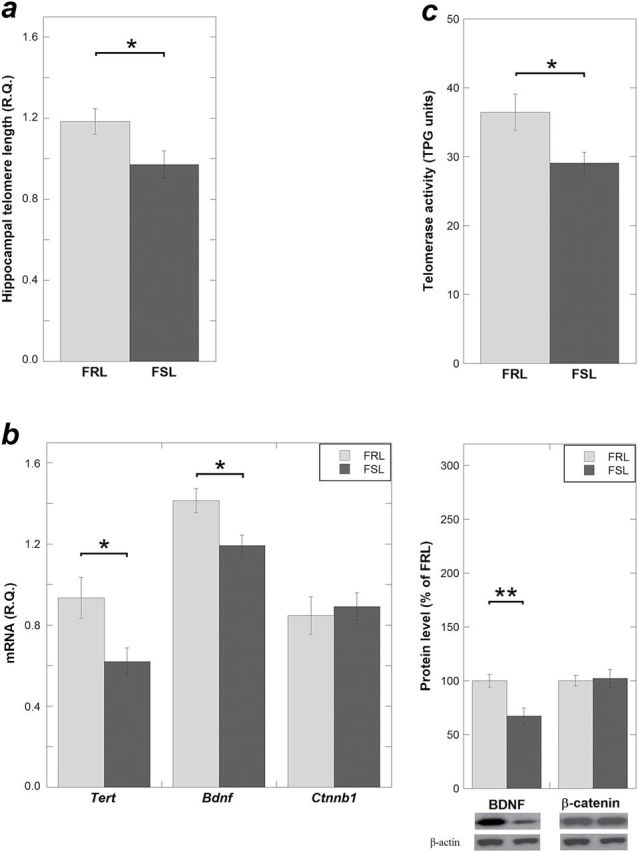
Telomere length (TL), Tert, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), β-catenin expression, and telomerase activity in hippocampus of naïve Flinders Sensitive Line (FSL)/Flinders Resistant Line (FRL) rats. (a) Naïve FSL rats had shorter telomere length compared with the same age FRL rats, measured using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). (b) Tert and Bdnf mRNA levels were reduced in the FSL compared with the FRL rats, measured using qRT-PCR (left panel). BDNF protein levels were reduced in FSL rats (right panel). (c) Telomerase activity was reduced in naïve FSL, detected by real-time telomeric repeat amplification protocol. Telomere length and gene expression data are presented as relative quantifications (R.Q.). Protein data are presented as percent of FRL. Lower right panels in (b) show representative Western-blot images of BDNF and β-catenin with β-actin as loading control. Telomerase activity is presented as TPG units. (a: n = 11 FRL, n = 16 FSL; n = 2 FSL outliers excluded; b-c: n = 6–8 animals per group; n = 1 FSL outlier excluded). Data are presented as means ± SEM, *P< .05, **P < .01.
