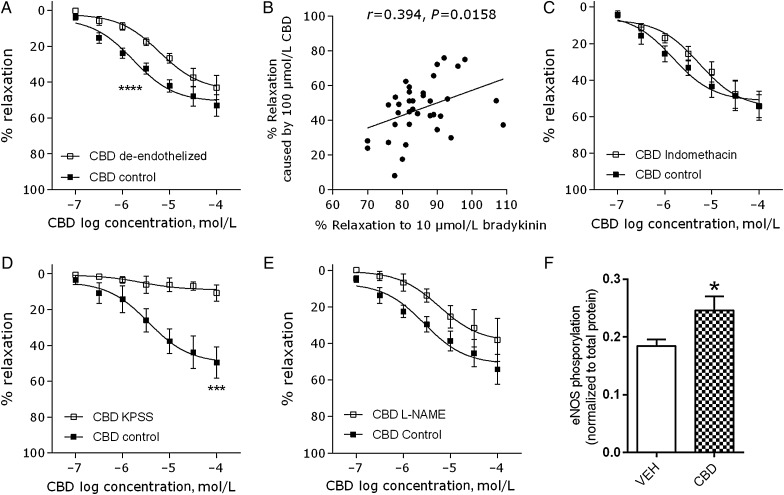
Figure 2.
Mechanisms of CBD-induced relaxation of human mesenteric arteries. Mean (± SEM) CBD-induced vasorelaxation of human mesenteric arteries after removal of the endothelium (n = 8, A), in arteries incubated with l-NAME (300 µmol/L, n = 6, B), in the presence of the non-selective COX inhibitor indomethacin (10 µmol/L, n = 6, D) or in arteries contracted using a high potassium (KPSS) Krebs (n = 5, E). (C) Maximal responses to CBD correlated with the vasorelaxant response to the endothelium-dependent vasorelaxant bradykinin. (F) In cultured human aortic endothelial cells, CBD (10 µmol/L, 10 min) increased eNOS phosphorylation at ser1177 (n = 9). Control responses to CBD and interventions were carried out in adjacent segments of mesenteric artery from the same patient. Rmax and EC50 values were compared by paired Students t-test, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.