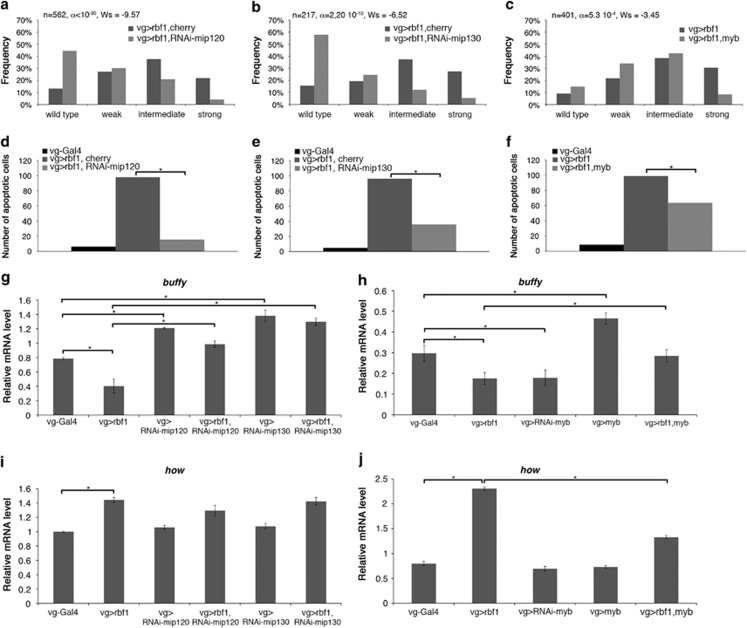
Figure 5.
Mip proteins and Myb are differentially involved in Rbf1-induced apoptosis. (a–c) Distribution of notch wing phenotypes in vg-Gal4>UAS-rbf1,UAS-cherry and vg-Gal4>UAS-rbf1,UAS-RNAi-mip120 (a), in vg-Gal4>UAS-rbf1,UAS-cherry and vg-Gal4>UAS-rbf1; UAS-RNAi-mip130 (b) and in vg-Gal4>UAS-rbf1 and vg-Gal4>UAS-rbf1; UAS-myb (c). Wing phenotypes were grouped in four categories according to the number of notches (wild type, weak, intermediate, strong). Statistical analysis was performed using Wilcoxon tests. Each experiment was independently performed three times; as the results were similar, only one experiment is presented here. (d–f) Quantification of TUNEL-positive cells in the wing pouch of genotypes studied in (a–c). Asterisks indicate a statistically significant difference between two genotypes (Student's t-test, P<0.05). (g–j) Quantification of buffy (g, h) and how (i, j) mRNA in wing imaginal discs by RT-qPCR. Data are normalized against rp49 and correspond to the mean of three independent experiments. Error bars are the S.E.M. Asterisks indicate statistically significant difference between two genotypes (Student's t-test, P<0.05)