Figure 1.
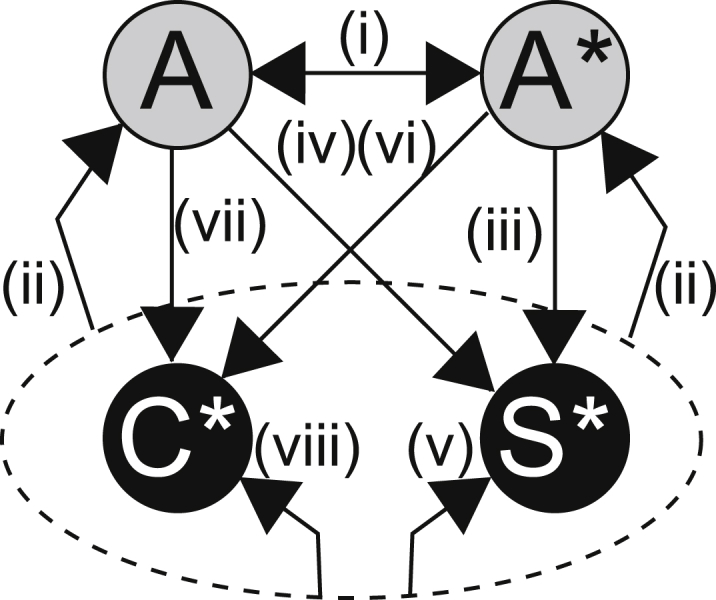
Summary of Edge Classifications
The full network was partitioned into eight different networks, each containing a different class of edge (see the main text), and different combinations of these were used in an information-theoretic framework to evaluate our hypotheses (see also Figure S1). Gray nodes (A) are adults; black nodes are juveniles, split into control (C) and CORT/developmentally stressed (S) treatments. The ∗ represents individuals from the same family (thus, here one adult is a parent and the other is unrelated). Edges from all juveniles (dashed oval) represent edges from related and unrelated juveniles combined (both C and S treatments and all unrelated juveniles are included).
