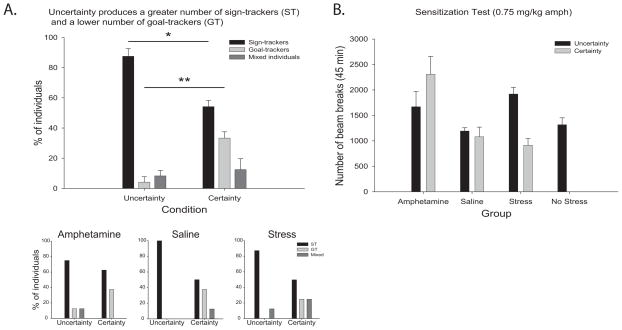
Fig. 2. Distribution of sign-trackers and goal-trackers, and test of locomotor (cross-) sensitization.
(A) Percentage of sign-trackers (ST), goal-trackers (GT), and mixed individuals in uncertainty groups as opposed to certainty groups on day 8, showing a greater proportion of sign-trackers and lower proportion of goal-trackers following reward uncertainty. Inserts show the percentage of individuals for each autoshaping phenotype across Amphetamine, Saline and Stress conditions. (B) Following an amphetamine challenge (0.75 mg/kg), rats sensitized to amphetamine and exposed to either certain or uncertain reward conditions showed increased locomotor activity in comparison to their saline treated counterparts. Of the chronically stressed rats only those exposed to uncertain reward conditions showed cross-sensitization and enhanced locomotor activity. Rats that received saline injections or No Stress conditions showed similar performance whether trained under uncertainty or certainty. Legends: * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; data is Mean +/− SEM.