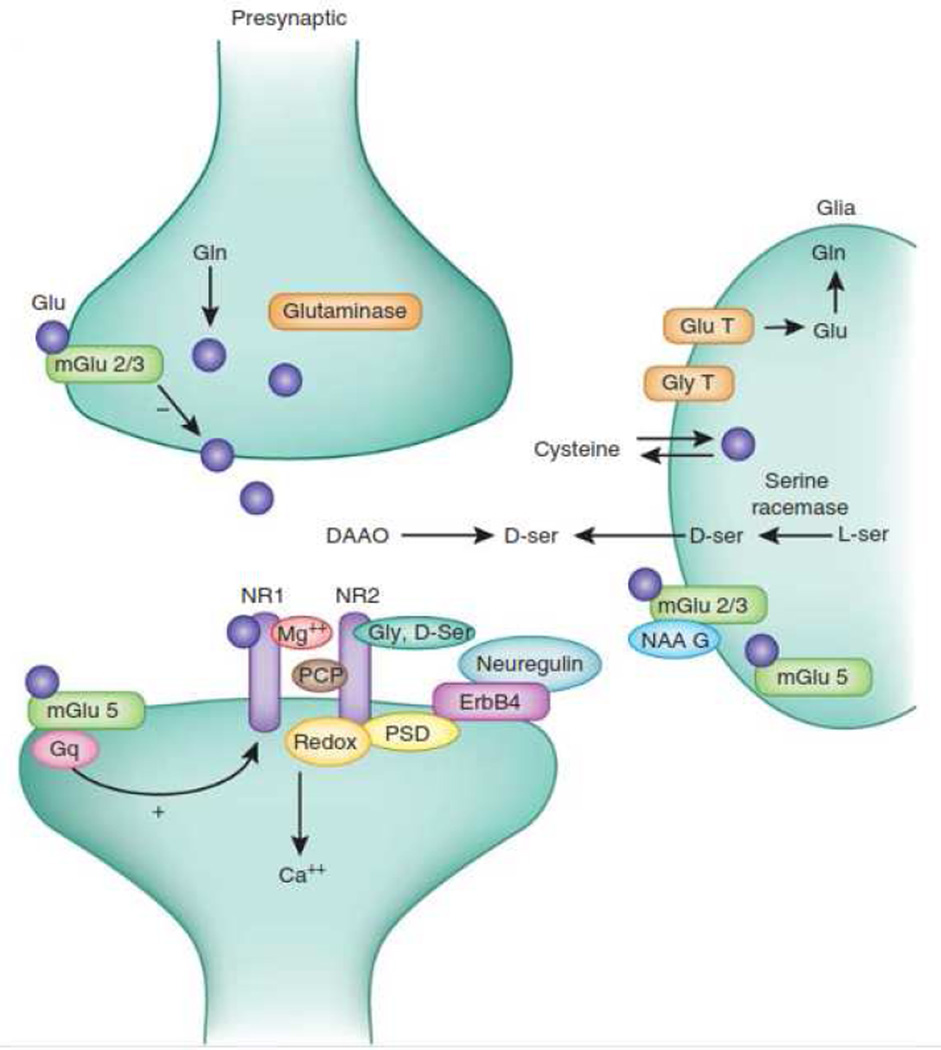
Figure 1.
Schematic model of the glutamate synapse, showing binding sites for glycine (Gly) and D-serine (D-ser), along with Type 1 glycine transporters (Gly T) that represent a target for drug development. Other targets include metabotropic type 2/3 (mGlu 2/3) or type 5 (mGlu 5), or D-amino acid oxidase (DAAO). (Used with permission from Moghaddam, B. and D. Javitt, From revolution to evolution: the glutamate hypothesis of schizophrenia and its implication for treatment. Neuropsychopharmacology, 2012. 37(1): p. 4–15.)