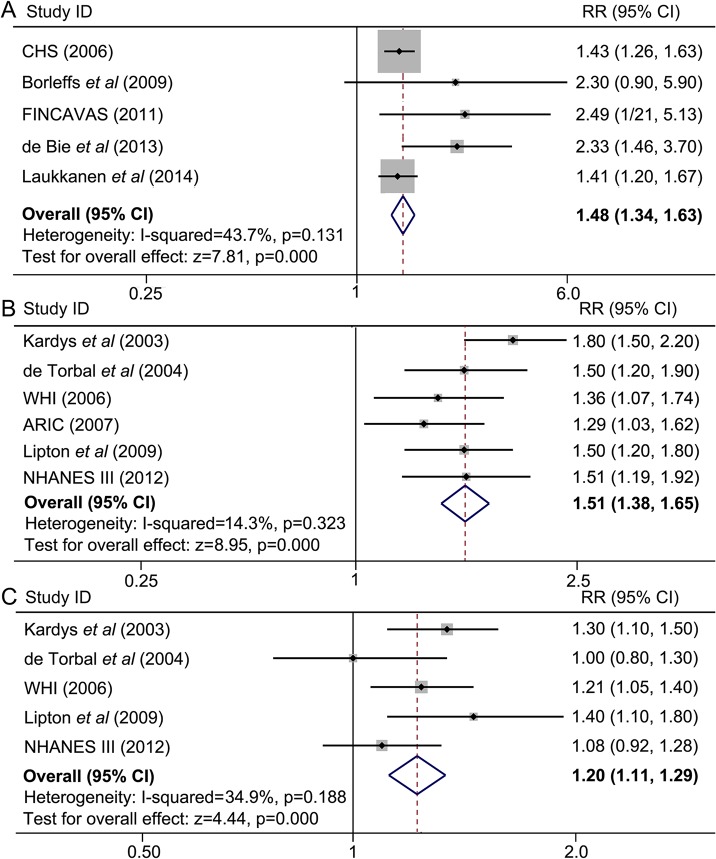
Fig 3. A wide spatial QRS-T angle is associated with a higher incidence of all-cause death.
Meta-analyses were from separated comparisons by two methods of categorizing. (A) Spatial QRS-T angles were divided into “wide angle” and “normal angle”, a meta-analysis of wide angles versus normal ones was conducted. (B) and (C) spatial QRS-T angles were segmented into three groups, i.e. normal, borderline and abnormal angles. (B) Results from comparison between abnormal and normal, (C) results from comparison between borderline and normal. ARIC: the Atherosclerosis in Communities Study; CHS: the Cardiovascular Health Study; CI: confidence interval; FINCAVAS: The Finnish Cardiovascular Study; NHANES III: the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey; RR: relative risk; WHI: The Women’s Health Initiative.