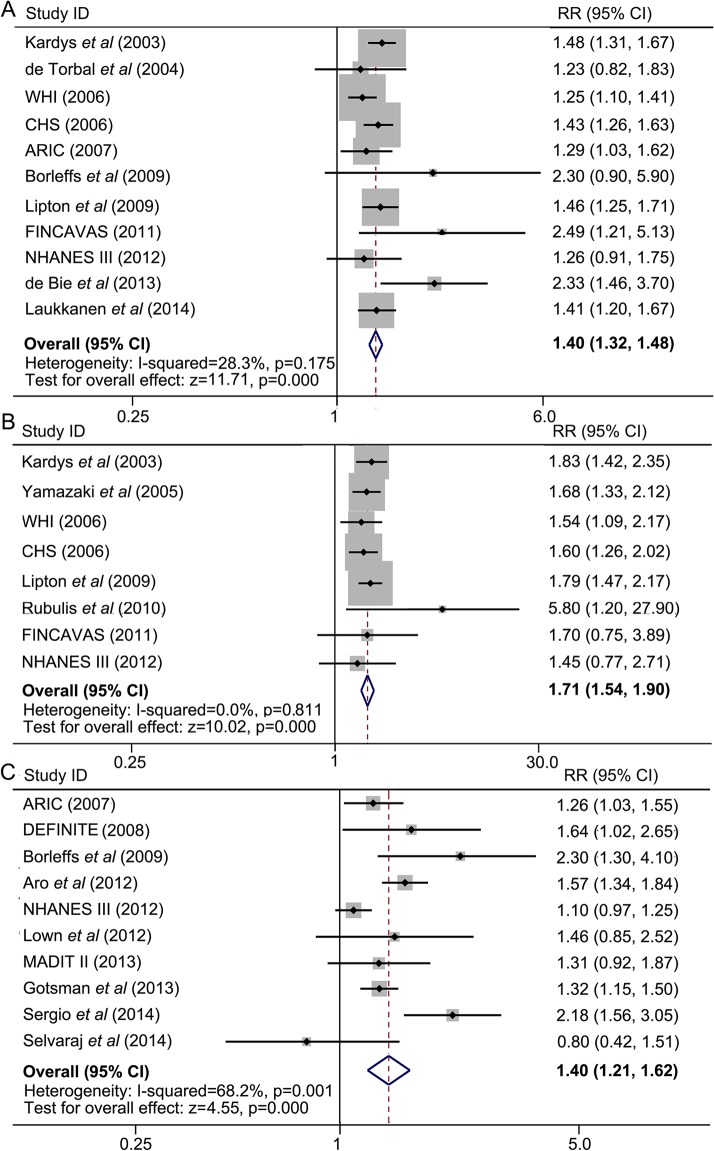
Fig 6. Combined analyses show that a wide spatial QRS-T angle predicts a higher incidence of all-cause death (A) and cardiac death (B), a wide frontal QRS-T angle is associated with a higher rate of all-cause death (C).
ARIC: the Atherosclerosis in Communities Study; CHS: the Cardiovascular Health Study; CI: confidence interval; DEFINITE: the Defibrillators in Nonischemic Cardiomyopathy Treatment Evaluation; FINCAVAS: The Finnish Cardiovascular Study; MADIT II: the Multicenter Automatic Defibrillator Implantation Trial II; NHANES III: the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey; RR: relative risk; WHI: The Women’s Health Initiative.