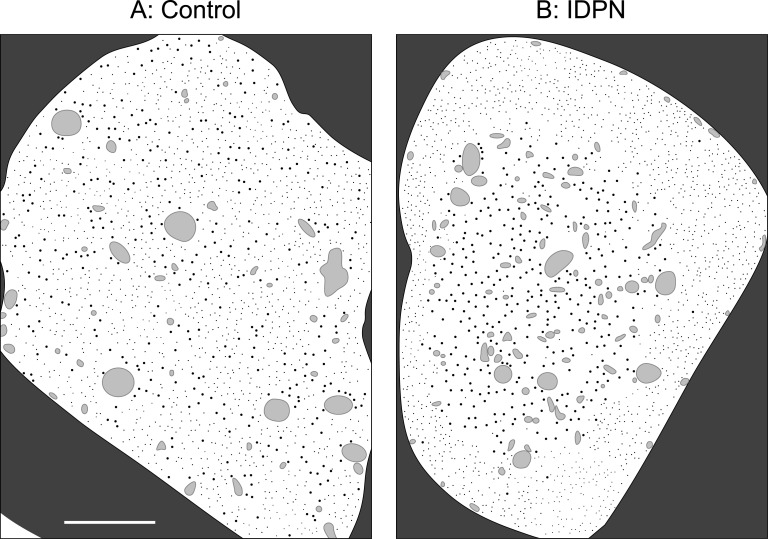
Fig 1. IDPN-induced segregation of microtubules and neurofilaments in axonal cross-sections.
We show here drawings that are based loosely on the electron micrographs in Fig 3 in the reference Papasozomenos et al. [50]. Due to copyright restrictions we are not able to show the actual micrographs. The authors administered IDPN in physiological saline to adult male rats by intraperitoneal injection (2 mg/g body weight). Control injections consisted of physiological saline alone. For the micrographs on which these drawings are based, the animal was sacrificed after 2 weeks and the nerve was fixed and examined in cross-section by electron microscopy. Full experimental details can be found in the original article. (A) Drawing of a control axon in cross-section showing that the microtubules (large black dots), neurofilaments (small black dots) and membranous organelles (irregularly shaped grey blobs) are normally interspersed throughout the axonal cross-section. (B) Drawing of an axon in cross-section after IDPN treatment showing that the microtubules and organelles form a central core surrounded by a peripheral rim of neurofilaments. Note that the central core of microtubules and organelles contains very few neurofilaments and the outer rim of neurofilaments contains very few microtubules and organelles. The dark grey area outside of the axon is the myelin sheath. The scale bar is 1 μm.