Figure 1.
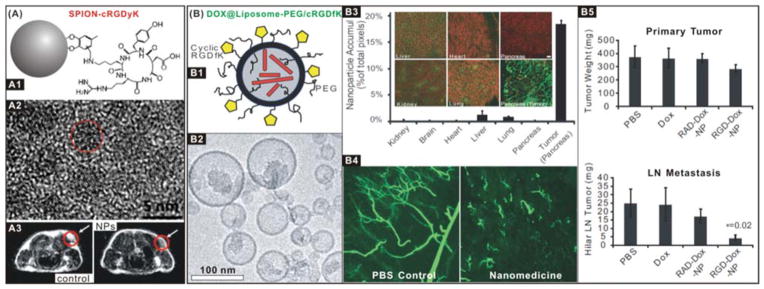
(A) SPION-cRGDyK nanomedicine for integrin αvβ3-targeted imaging and diagnosis: (A1) Schematic structure of ultra-small SPION-cRGDyK nanoparticle; (A2) HRTEM image of the iron oxide nanoparticle; (A3) MRI cross-section patterns of U87MG tumour mice treated with SPIONs without (control) and with (NPs) RGD targeting.118 Reproduced with permission from ref. 118, Copyright 2008 American Chemical Society. (B) DOX@Liposome-PEG/cRGDfK nanomedicine for integrin αvβ3-targeted therapy: (B1) Schematic structure of the DOX@Liposome-PEG/cRGDfK nanomedicine; (B2) TEM image of the nanomedicine; (B3) Distributions of the nanomedicine in R40P pancreatic tumour, where the green colour represents the nanomedicine binding; (B4) The vascular disruption in the mouse model treated with control and nanomedicine samples; (B5) Anti-primary tumour and anti-metastasis efficacies of the nanomedicine.119 Reproduced with permission from ref. 119, Copyright 2008 National Academy of Sciences, USA.
