Figure 9.
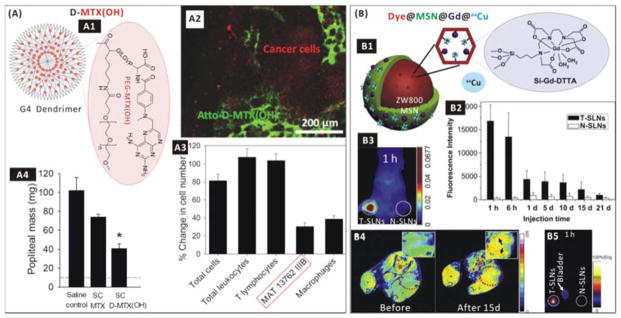
(A) Lymph-targeted drug delivery using the dendrimer-based nanomedicine. (A1) Construction of the D-MTX(OH) nanomedicine; (A2) Confocal fluorescent image of a popliteal lymph node bearing MAT metastases (red-labelled) 3 days after subcutaneous injection of green-labelled D-MTX(OH) into the inner heel of rats; (A3) Cytotoxicity of the D-MTX(OH) nanomedicine to lymph node cells 8 days after treatment of rats bearing popliteal lymph node-resident metastases of MAT 13762 IIIB carcinoma; (A4) Anti-metastasis efficacy of the nanomedicine against popliteal lymph node-resident metastases of MAT 13762 IIIB carcinoma.234 Reproduced with permission from ref. 234, Copyright 2014 Elsevier. (B) Imaging and diagnosis of the SLNs of metastasis. (B1) Construction of the Dye@MSN@Gd@64Cu nanomedicine; (B2) Retention of the nanomedicine in T-SLNs and N-SLNs of a 4T1 tumour metastatic model after subcutaneous administration; (B3) NIRF imaging, (B4) MRI and (B5) PET imaging of SLNs in the 4T1 tumour metastatic model after injection of the nanomedicine.233 Reproduced with permission from ref. 233, Copyright 2012 Elsevier.
