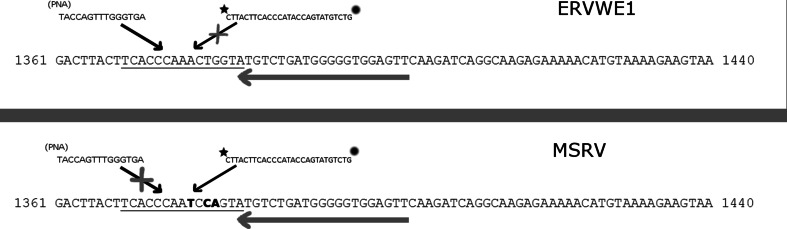
Fig. 1.
A principle of the method behind the quantitation of MSRV expression using PNA-mediated quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Peptide nucleic acid (PNA) probe (on the left-hand side of the figure) binds to the ERVWE1 template with high affinity due to 100 % complementarity of their sequences and prevents the hybridisation of fluorescently labelled probe (on the right). The probe remains intact and therefore no signal is emitted. If MSRV serves as template, PNA probe cannot bind tightly to the DNA due to three mismatches between PNA and template that diminish drastically its affinity. On the contrary, fluorescent probe now is allowed to bind to the MSRV template and afterwards it is cleaved by the polymerase during the elongation phase and emits a signal as normally seen in probe-based QPCR