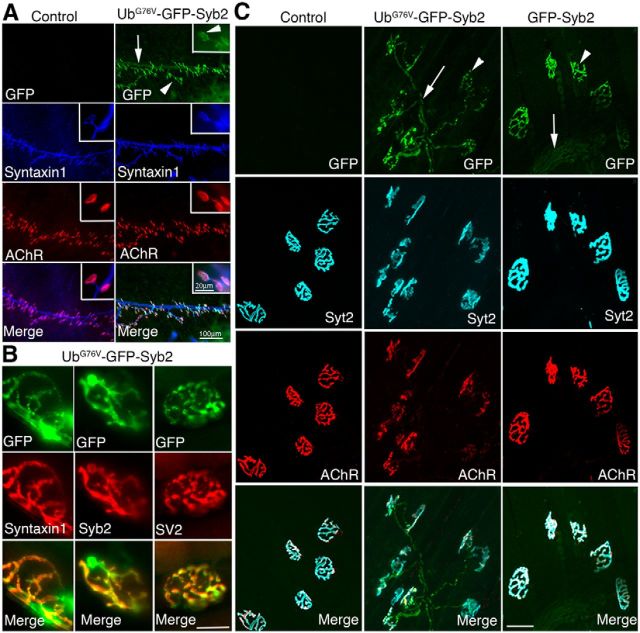
Figure 2.
Localization of UbG76V-GFP-Syb2 or GFP-Syb2 in motor axons and nerve terminals. A, Whole-mount immunofluorescence staining of triangularis sterni muscles in UbG76V-GFP-Syb2 and nontransgenic control mice at P0, viewed under GFP fluorescence (green), anti-Syntaxin1 staining (blue), and Texas-Red-conjugated α-bungarotoxin for AChRs (red). GFP fluorescence is detected along the nerve trunk (arrow) and nerve terminals (arrowheads) in UbG76V-GFP-Syb2 mice. Insets at the top right corner of each panel show high-power views of individual nerve terminals; GFP puncta were readily detectable at the nerve terminal. B, Images of single nerve terminals obtained from teased thigh muscle fibers in UbG76V-GFP-Syb2 mice (5 months of age). Top green panels show GFP fluorescence; middle red panels show nerve terminals labeled by antibodies against Syntaxin1, Syb2, or SV2. Merged images show the localization of GFP fluorescence at the nerve terminals. C, Confocal images of whole-mount triangularis sterni muscle from nontransgenic control, UbG76V-GFP-Syb2, and GFP-Syb2 mice (5 months of age), viewed under GFP fluorescence (green), anti-synaptotagmin-2 (cyan), and Alexa Fluor 647-conjugated α-bungarotoxin for AChR (red). GFP fluorescence is localized along preterminal axons (arrows) and nerve terminals (arrowheads) in both UbG76V-GFP-Syb2 and GFP-Syb2 transgenic mice. Scale bars: A, 100 μm; A, insets, 20 μm; B, 20 μm; C, 50 μm.