Figure 3.
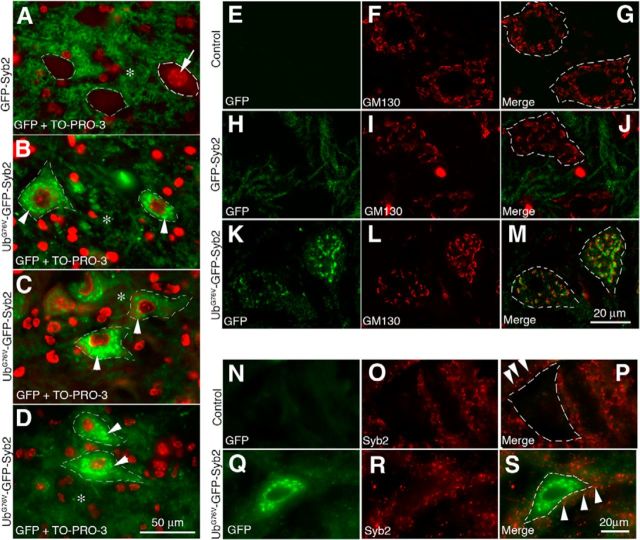
Expression and localization of UbG76V-GFP-Syb2 and GFP-Syb2 in motor neurons. A–D, Cross sections of the ventral horn of lumbar spinal cords from GFP-Syb2 (A, 5-month-old) and UbG76V-GFP-Syb2 mice (B, 1-month-old; C, 5-month-old; D, 8-month-old), counterstained with TO-PRO-3 to label nuclei (A, arrow). Merged images are shown to illustrate the distribution of GFP fluorescence (green) and nuclei (red; an example is shown by an arrow in A). In both GFP-Syb2 and UbG76V-GFP-Syb2 mice, GFP-positive labeling is detected in the neuropil (*) surrounding the somata. In addition, GFP-positive puncta (arrowheads in B–D) are detected within the somata of motor neurons in UbG76V-GFP-Syb2 mice. A similar labeling pattern is observed in UbG76V-GFP-Syb2 mice at 1, 5, and 8 months of age. E–M, Confocal images of spinal motor neurons from non-Tg control (top), GFP-Syb2 (middle), and UbG76V-GFP-Syb2 mice (bottom), immunolabeled with anti-GM130 antibodies (red). Merged image shows that GFP-positive puncta are closely associated with cis-Golgi (labeled by anti-GM130 antibodies). N–S, High-magnification images of motor neurons in the ventral horn of lumbar spinal cord, immunolabeled with anti-Syb2 antibodies (red) that recognize endogenous Syb2 but not the fusion protein UbG76V-GFP-Syb2. In both UbG76V-GFP-Syb2 and non-Tg control mice, Syb2-positive puncta (arrowheads in P and S) are detected outside of the motor neuron somata. Dashed lines in A–D, G, J, M, P, and S demarcate the boundary of the motor neuron somata. Scale bars: A–D, 50 μm; E–M, 20 μm; N–S, 20 μm.