Figure 5.
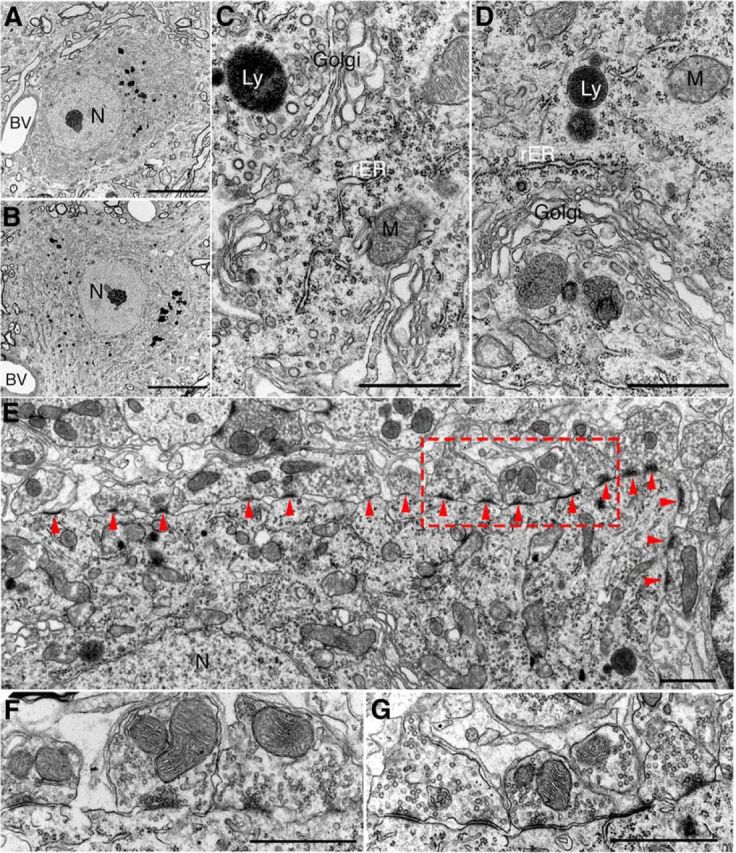
Ultrastructure of motor neuron in UbG76V-GFP-Syb2 mice. A, B, Representative electron micrographs (low-power view) of an example of lumbar spinal motor neuron from nontransgenic control mice (A) and UbG76V-GFP-Syb2 mice (B, 8 months of age); both somata contain a large round-shaped nucleus (N) with a prominent nucleolus and organelle-rich cytoplasm. Blood vessels (BV) are frequently observed. C, D, High-power electron micrographs of motor neuron soma from control (C) and UbG76V-GFP-Syb2 mice (D), showing subcellular organelles including mitochondria (M), Golgi apparatus (Golgi), rough endoplasmic reticulum (rER), and lysosomes (Ly). E–G, Synapses on motor neuron in UbG76V-GFP-Syb2 mice (E, G) and control mice (F; 8 months of age). Numerous synapses (arrowheads) are found on the plasma membrane of motor neuron soma in UbG76V-GFP-Syb2 mice (E, low-power view; G, high-magnification view of the region in E marked by the rectangular area) showing features similar to those of the synapses on motor neuron soma in control mice (F). Scale bars: A, B, 10 μm; C, D, 1 μm; E, 1 μm; F, G, 1 μm.
