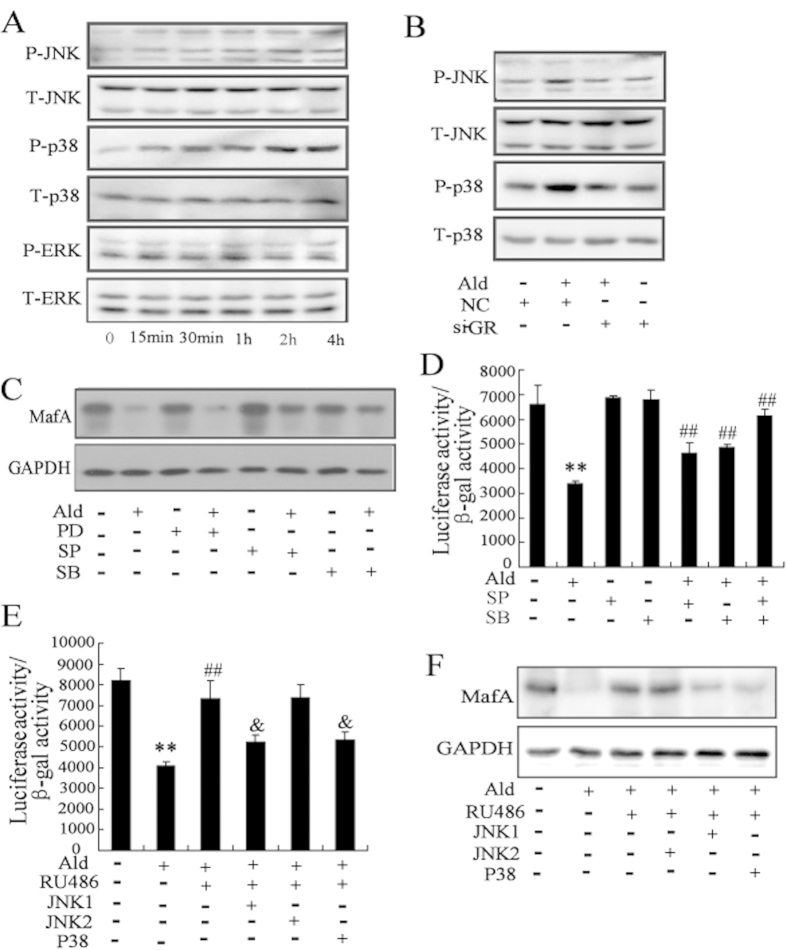
Figure 4. Activation of MAPK signaling pathway results in the decrease of MafA expression level and transcriptional activity by the treatment of aldosterone.
(A) Treated with aldosterone (100 nmol/l) significantly increased the phosphorylation levels of JNK and p38 in Min6 cells. (B) Min6 cells were transfected with si-GR for 24 h, and then treated with aldosterone. The phosphorylation levels of JNK and p38 in Min6 cells induced by aldosterone were significantly reversed by transfected with si-GR. After pretreatment with SP (the JNK-specific inhibitor), SB (the p38-specific inhibitor), and PD (the ERK-specific inhibitor) for 30 min, Min6 cells were treated with aldosterone. The decrease of MafA protein level (C) and MafA transcriptional activity (D) in Min6 cells induced by aldosterone were significantly reversed by SP and SB. (E) Min6 cells were cotransfected with JNK1, JNK2, or P38 expressing plasmids with the MAREs-luc reporter plasmid, and then treated with aldosterone and/or RU486. RU486 attenuated the inhibitory effects of aldosterone on MafA transcriptional activity, which was reversed by overexpression of JNK1 or p38. (F) Min6 cells were transfected with JNK1, JNK2, or P38 expressing plasmids, and then treated with aldosterone and/or RU486. RU486 attenuated the inhibitory effects of aldosterone on MafA protein level, which was reversed by overexpression of JNK1 or p38. **P < 0.01, compared to control; ##P < 0.01, compared to aldosterone treatment. & P < 0.01, compared to aldosterone + RU486.