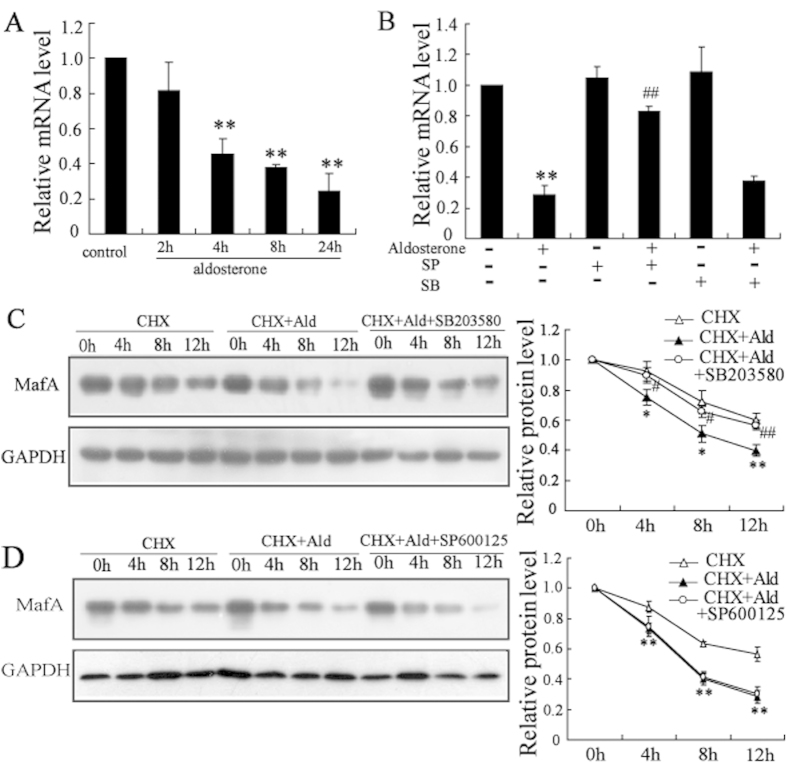
Figure 5. Aldosterone-induced inhibition of MafA expression is regulated at the transcriptional level by JNK while at post-transcriptional level by P38.
(A) Treatment with aldosterone (100 nmol/l) significantly suppressed MafA mRNA expression in a time-dependent manner in Min6 cells. (B) SP (the JNK-specific inhibitor) attenuated the inhibitory effects of aldosterone on MafA mRNA level in Min6 cells. (C) Min6 cells were divided into three groups (control, aldosterone (Ald) and Ald + SB203580). After the indicated treatments for 2 h, cells were co-cultured with 50 mmol/l cycloheximide (CHX) for 0, 4, 8, or 12 h. Aldosterone induced a more rapid reduction in MafA protein levels in the presence of CHX, which could be reversed by SB203580. The half-life of MafA was calculated. (D) Min6 cells were divided into three groups (control, Ald and Ald + SP600125). SP600125 could not reverse the reduction of MafA protein level induced by aldosterone. The half-life of MafA was calculated. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01, compared to control; #P < 0.05 and ##P < 0.01, compared to aldosterone treatment.