Figure 2.
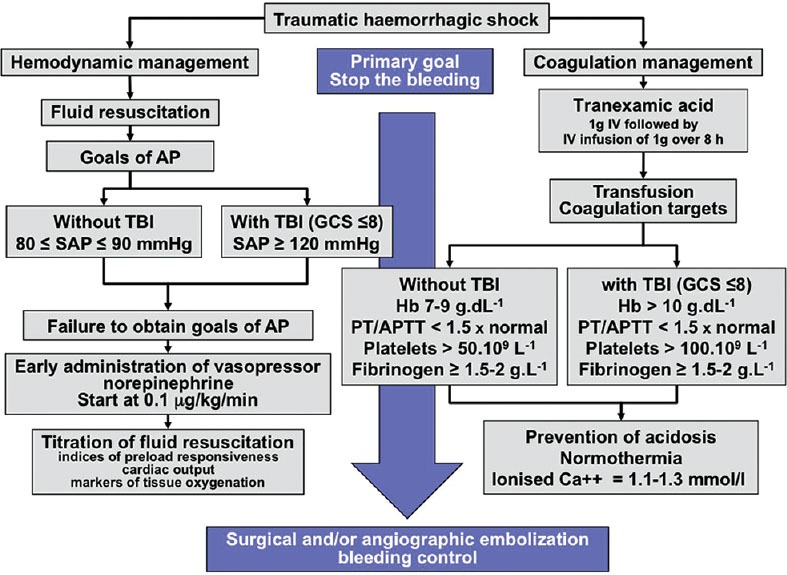
Flow chart of initial management of traumatic hemorrhagic shock. In the acute phase of traumatic hemorrhagic shock, the therapeutic priority is to stop the bleeding. As long as this bleeding is not controlled, the physician must manage fluid resuscitation, vasopressors, and blood transfusion to prevent or treat acute coagulopathy of trauma (AP = Arterial pressure, SAP = Systolic arterial pressure, TBI = Trauma brain injury, Hb = Hemoglobin, PT = Prothrombin time, APTT = Activated partial thromboplastin time)[36]
