Abstract
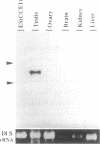
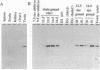
In an effort to study the molecular basis of the determination processes of the mammalian germ cell lineage, we have tried to isolate a mouse gene homolog to vasa, which plays an essential role as a maternal determining factor for the formation of Drosophila germ cell precursors. By reverse transcriptase PCRs of mouse primordial germ cell cDNAs using family-specific primers, we obtained a gene (Mvh) encoding a DEAD-family protein that showed a much higher degree of similarity with the product of the Drosophila vasa gene (vas) than previously reported mouse genes. In adult tissues, Mvh transcripts were exclusively detected in testicular germ cells, in which Mvh protein was found to be localized in cytoplasm of spermatocytes and round spermatids including a perinuclear granule. The protein was also expressed in germ cells colonized in embryonic gonads but was not detected in pluripotential embryonic cells such as stem cells and germ cells. These results suggest the possibility that the Mvh protein may play an important role in the determination events of mouse germ cells as in the case of Drosophila vasa.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe K. Rapid isolation of desired sequences from lone linker PCR amplified cDNA mixtures: application to identification and recovery of expressed sequences in cloned genomic DNA. Mamm Genome. 1992;2(4):252–259. doi: 10.1007/BF00355435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beams H. W., Kessel R. G. The problem of germ cell determinants. Int Rev Cytol. 1974;39:413–479. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60944-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddy E. M. Germ plasm and the differentiation of the germ cell line. Int Rev Cytol. 1975;43:229–280. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ephrussi A., Lehmann R. Induction of germ cell formation by oskar. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):387–392. doi: 10.1038/358387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett D. W., Eddy E. M., Phillips D. M. Observations on the fine structure and relationships of the chromatoid body in mammalian spermatogenesis. Biol Reprod. 1970 Feb;2(1):129–153. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod2.1.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geremia R., d'Agostino A., Monesi V. Biochemical evidence of haploid gene activity in spermatogenesis of the mouse. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Jan;111(1):23–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90232-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg M., Snow M. H., McLaren A. Primordial germ cells in the mouse embryo during gastrulation. Development. 1990 Oct;110(2):521–528. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.2.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay B., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. A protein component of Drosophila polar granules is encoded by vasa and has extensive sequence similarity to ATP-dependent helicases. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):577–587. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90216-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay B., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. Localization of vasa, a component of Drosophila polar granules, in maternal-effect mutants that alter embryonic anteroposterior polarity. Development. 1990 Jun;109(2):425–433. doi: 10.1242/dev.109.2.425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirling H., Scheffner M., Restle T., Stahl H. RNA helicase activity associated with the human p68 protein. Nature. 1989 Jun 15;339(6225):562–564. doi: 10.1038/339562a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi S., Amikura R., Okada M. Presence of mitochondrial large ribosomal RNA outside mitochondria in germ plasm of Drosophila melanogaster. Science. 1993 Jun 4;260(5113):1521–1524. doi: 10.1126/science.7684857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komiya T., Itoh K., Ikenishi K., Furusawa M. Isolation and characterization of a novel gene of the DEAD box protein family which is specifically expressed in germ cells of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1994 Apr;162(2):354–363. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1994.1093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasko P. F., Ashburner M. The product of the Drosophila gene vasa is very similar to eukaryotic initiation factor-4A. Nature. 1988 Oct 13;335(6191):611–617. doi: 10.1038/335611a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire L., Heinlein U. A. High-level expression in male germ cells of murine P68 RNA helicase mRNA. Life Sci. 1993;52(11):917–926. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(93)90526-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroy P., Alzari P., Sassoon D., Wolgemuth D., Fellous M. The protein encoded by a murine male germ cell-specific transcript is a putative ATP-dependent RNA helicase. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):549–559. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90125-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang L., Diehl-Jones W., Lasko P. Localization of vasa protein to the Drosophila pole plasm is independent of its RNA-binding and helicase activities. Development. 1994 May;120(5):1201–1211. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.5.1201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder P., Lasko P. F., Ashburner M., Leroy P., Nielsen P. J., Nishi K., Schnier J., Slonimski P. P. Birth of the D-E-A-D box. Nature. 1989 Jan 12;337(6203):121–122. doi: 10.1038/337121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahowald A. P. Germ plasm revisited and illuminated. Science. 1992 Mar 6;255(5049):1216–1217. doi: 10.1126/science.1372132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui Y., Zsebo K., Hogan B. L. Derivation of pluripotential embryonic stem cells from murine primordial germ cells in culture. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):841–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90317-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen P. J., Trachsel H. The mouse protein synthesis initiation factor 4A gene family includes two related functional genes which are differentially expressed. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2097–2105. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03049.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noce T., Fujiwara Y., Ito M., Takeuchi T., Hashimoto N., Yamanouchi M., Higashinakagawa T., Fujimoto H. A novel murine zinc finger gene mapped within the tw18 deletion region expresses in germ cells and embryonic nervous system. Dev Biol. 1993 Feb;155(2):409–422. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noce T., Fujiwara Y., Sezaki M., Fujimoto H., Higashinakagawa T. Expression of a mouse zinc finger protein gene in both spermatocytes and oocytes during meiosis. Dev Biol. 1992 Oct;153(2):356–367. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90120-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parvinen M., Parvinen L. M. Active movements of the chromatoid body. A possible transport mechanism for haploid gene products. J Cell Biol. 1979 Mar;80(3):621–628. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.3.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson L. F., Harvey M., Lasko P. F. Dbp73D, a Drosophila gene expressed in ovary, encodes a novel D-E-A-D box protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jun 25;20(12):3063–3067. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.12.3063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Dressler G. R., Balling R., Rohdewohld H., Gruss P. Oct-4: a germline-specific transcription factor mapping to the mouse t-complex. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2185–2195. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07388.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solter D., Knowles B. B. Monoclonal antibody defining a stage-specific mouse embryonic antigen (SSEA-1). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5565–5569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman M., Bennett D. A light- and electron-microscopic study of primordial germ cells in the early mouse embryo. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1973 Aug;30(1):97–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens L. C. Origin of testicular teratomas from primordial germ cells in mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1967 Apr;38(4):549–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strome S. Developmental biology. The germ of the issue. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):368–369. doi: 10.1038/358368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Valoir T., Tucker M. A., Belikoff E. J., Camp L. A., Bolduc C., Beckingham K. A second maternally expressed Drosophila gene encodes a putative RNA helicase of the "DEAD box" family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2113–2117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]