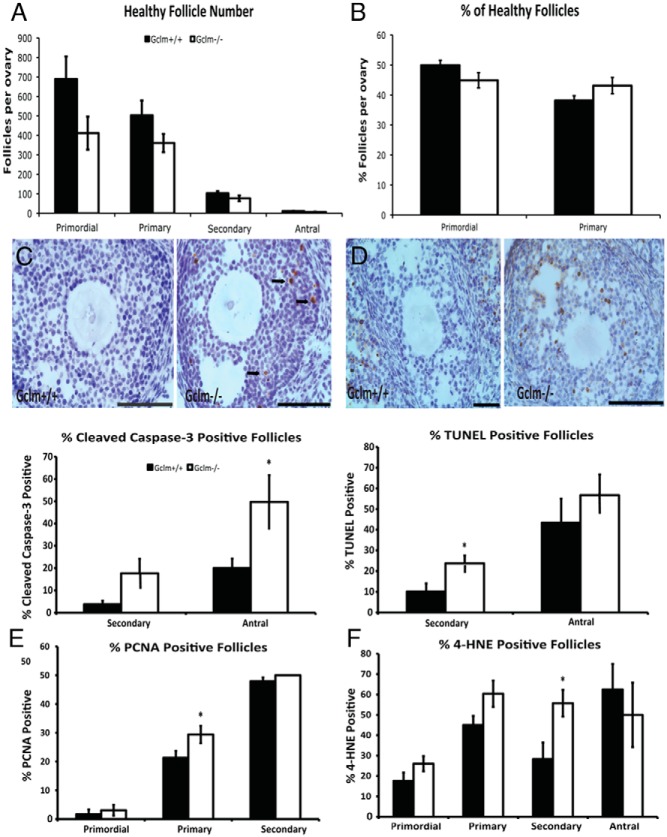
Figure 7.
Effects of Gclm deletion on ovarian follicle counts, apoptosis, cell proliferation, and oxidative damage at 2 months of age. Healthy and atretic follicles were counted in hematoxylin and eosin-stained serial sections, as described in Materials and Methods. A, Mean ± SEM of numbers of healthy primordial, primary, secondary, and antral follicles in Gclm+/+ and Gclm−/− ovaries at 2 months of age (n = 10 for Gclm+/+ and n = 6 for Gclm−/−). B, Mean ± SEM percentage of healthy primordial follicles and primary follicles of total healthy follicles (calculated from counts shown in Figure 7A). C and D, Cleaved caspase-3 and TUNEL were performed to detect apoptotic cells as described in Materials and Methods. C, Means ± SEM percentage of secondary and antral follicles that had cleaved caspase-3-positive granulosa cells (GC; n = 5/group). Representative images at top of caspase-3 immunostaining in Gclm+/+ (left) and Gclm−/− (right) ovaries are shown. Black arrows indicate cleaved caspase-3-positive GCs of antral follicle. D, Means ± SEM of follicles with TUNEL-positive GCs in the ovaries of 2-month-old mice (n = 5/group). Representative images at top of TUNEL in Gclm+/+ (left panel) and Gclm−/− (right panel) ovaries are shown. E and F, PCNA and 4-HNE were performed to detect proliferating GCs and oxidative damage as described in Materials and Methods. E, Means ± SEM percentage of primordial, primary, and secondary follicles with PCNA-positive GC (n = 5/group). F, Means ± SEM percentage of primordial, primary, secondary, and antral follicles with 4-HNE-positive GCs (n = 5/group). *, Significant difference between genotypes by nonparametric Mann-Whitney U test or t test at P < .05. All scale bars, 100 μm.