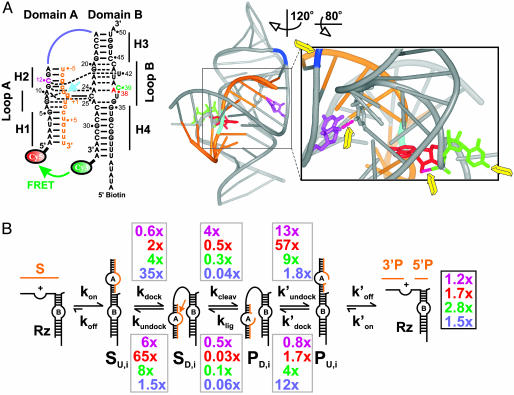
Fig. 1.
Dissecting the impact of single functional group modifications on hairpin ribozyme catalysis. (A) Secondary and tertiary structure of the docked WT ribozyme used in this study (9). (Left) Watson–Crick and noncanonical base pairs are indicated as solid and dashed lines, respectively. Orange, substrate; cyan arrow, cleavage site; color-coded nucleotides and junction connection were modified in this study (purple, dC12; red, dA38; green, C39S3; blue, RzAS3). (Right) 3D ribbon-and-stick representation with same color coding (www.pymol.org). Yellow arrows, modified functional groups distant from the (cyan) cleavage site; pink dashed tubes, modified hydrogen bonds. (B) Schematic of the reaction pathway. Gray boxes, observed effects of the color-coded functional group modifications on individual rate constants relative to those of the WT; black box, effects on the overall cleavage rate constant.