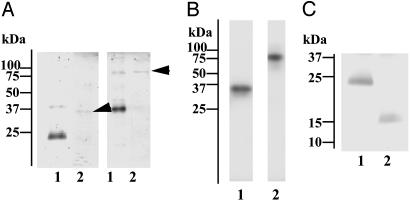
Fig. 2.
Characterization of lamprey GlcNAc-binding lectin and its associated protease. (A) SDS/PAGE of purified GlcNAc-binding lectin (lane 1) and its associated protease (lane 2, arrows). Samples were run under reducing (Left) or nonreducing (Right) conditions and stained for proteins with Coomassie brilliant blue R-250. (B) Incorporation of tritium-labeled diisopropylfluorophosphate into GlcNAc-binding lectin-associated protease. The purified protease was treated with tritium-labeled diisopropylfluorophosphate and subjected to SDS/PAGE under reducing (lane 1) or nonreducing (lane 2) conditions, followed by autoradiography. (C) Collagenase digestion of GlcNAc-binding lectin. Lamprey GlcNAc-binding lectin was incubated in the absence (lane 1) or presence (lane 2) of collagenase and subjected to SDS/PAGE, followed by protein staining.