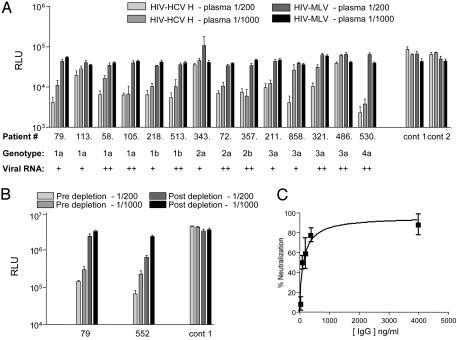
Fig. 1.
HCV-specific nAb response. (A) Plasma samples from uninfected individuals (cont 1 and cont 2) and those chronically infected with HCV genotypes 1, 2, 3, and 4, with low (+, <103 copies per ml) and high (++, >103 copies per ml) viral RNA levels, were tested for their ability to neutralize pseudotype viruses bearing H (HIV-HCV H) and MLV (HIV-MLV) gps at plasma dilutions of 1/200 and 1/1,000. The graph depicts infectivity, expressed as luciferase RLU, of HIV-HCV H and HIV-MLV (RLU ×10) in the presence of various plasma levels. Values are the mean of quadruplicate wells with the standard deviation shown. (B) Plasma from two chronically HCV-infected (79 and 552) individuals were tested for neutralization of HIV-HCV H at final dilutions of 1/200 and 1/1,000 before and after depletion of IgG. As a specificity control, virus infection in the presence of plasma from an uninfected individual (cont 1) is shown. Virus infectivity is shown as RLU, and values are the mean of quadruplicate wells with the standard deviation shown. (C) Neutralization of HIV-HCV H by plasma IgG purified from chronically infected patient 552. Data are shown as percentage neutralization, derived from quadruplicate wells with the standard deviation shown.