Figure 1.
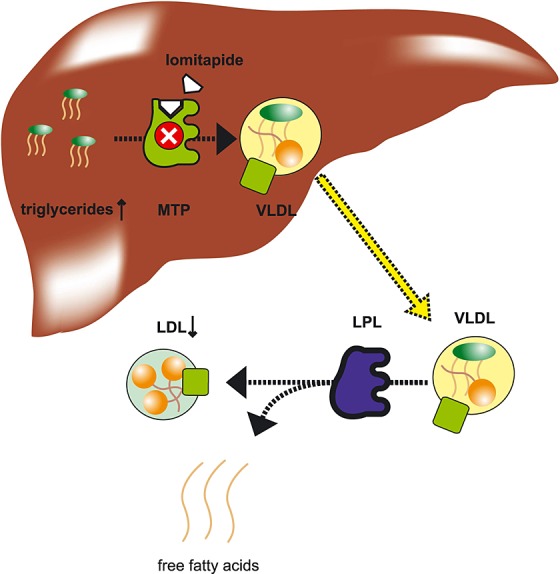
Mechanism of action of lomitapide. MTP is involved in the production of VLDL. After production in the liver, VLDL is released into the plasma. The enzyme lipoprotein lipase (LPL) catalyzes the breakdown of triglycerides from the VLDL into free fatty acids. As a result, VLDL is transformed into LDL. By inhibiting MTP, lomitapide reduces the production and release of VLDL, and LDL levels in plasma. A side effect of lomitapide is the accumulation of triglycerides in the liver, which is probably due to the inhibition of VLDL-mediated release of triglycerides from the liver.  apolipoprotein B100,
apolipoprotein B100,  triglycerides,
triglycerides,  cholesterol ester
cholesterol ester
