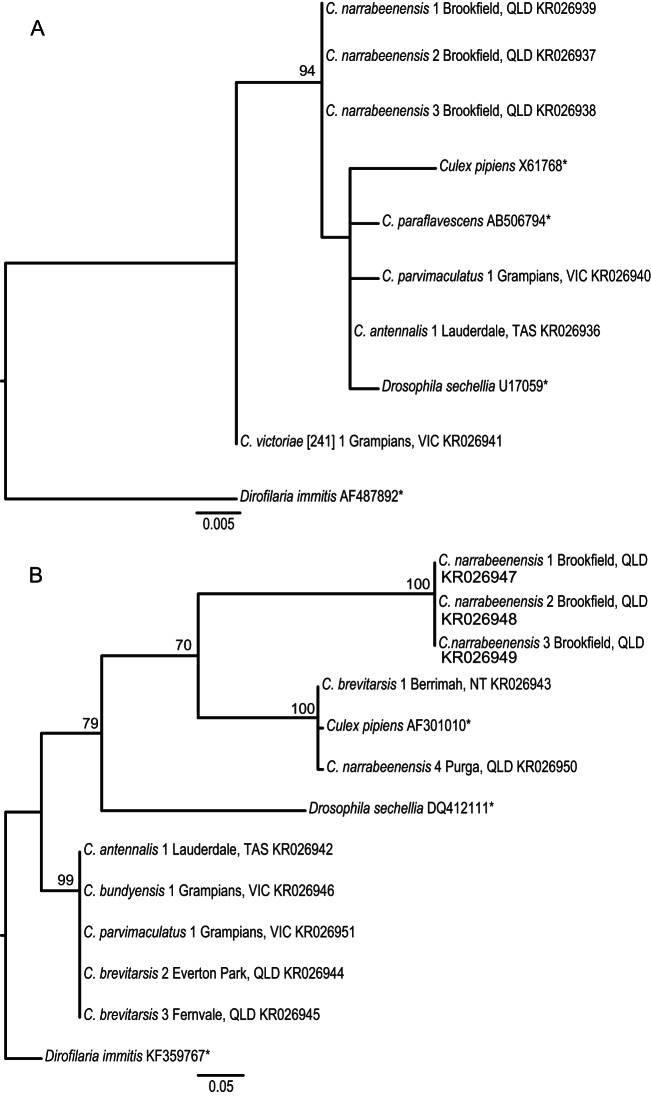
FIG 3.
Maximum-likelihood phylogenetic trees of Wolbachia. Phylogenetic trees based on a 390-bp region of the 16S rRNA gene (A) and a 351-bp region of the wsp gene (B) are shown. Sequences were aligned using the Clustal W algorithm employing the GTR substitution model (16S rRNA gene) and the HKY substitution model (wsp) based on JModelTest2 analysis with 1,000 bootstrap replicates. Bootstrap proportions of ≥70% are indicated beside nodes. Three supergroups were also included for reference; Drosophila sechellia (Wolbachia supergroup A), Culex pipiens (Wolbachia supergroup B), and Dirofilaria immitis (Wolbachia supergroup C). The Wolbachia sequence from Dirofilaria immitis was used to root the trees. The capture location is indicated beside the species name. Asterisks denote sequences obtained from GenBank; all other sequences were generated in this study.