FIG 1.
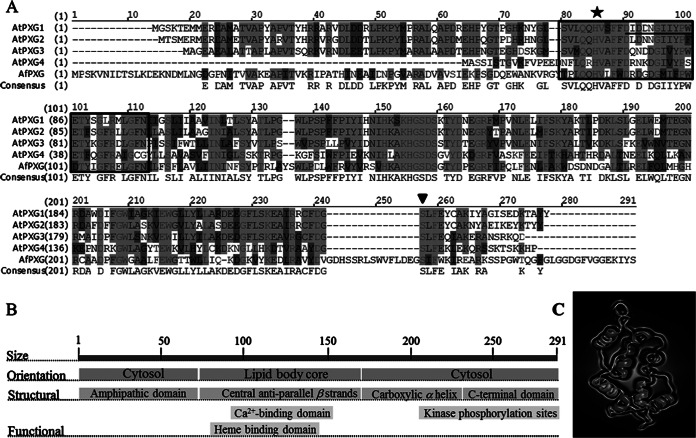
Structural features of AfPXG. (A) Multiple-sequence alignment of the deduced amino acids of the protein isolated from A. flavus (GenBank accession number KJ668859) with the A. thaliana proteins AtPXG1 (At4g26740), AtPXG2 (At5g55240), AtPXG3 (At2g33380), and AtPXG4 (At1g70670). The boxed domain (residues 62 to 97) corresponds to an EF-hand motif, and the underlined residues between residues 75 and 86 correspond to the Ca2+-binding domain. A star indicates the position of histidine 86, responsible for heme binding; an inverted triangle indicates a phosphorylation site; hyphens indicate absent residues; dark gray shading indicates similarity; light gray shading with lighter text indicates identity; light gray shading with darker text indicates a conservative residue; black text with a white background indicates nonsimilar residues. (B) Orientation and location of structural and functional domains. (C) Predicted three-dimensional structure of the putative caleosin (AFLA_00280). The virtual image was generated online using http://www.sbg.bio.ic.ac.uk/phyre2.