FIG 11.
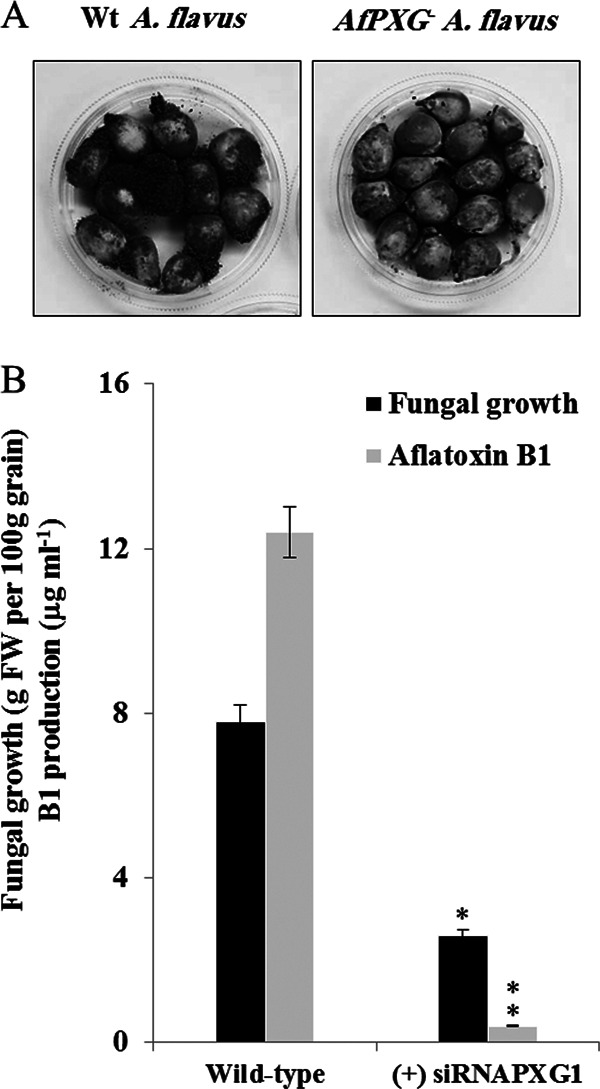
Impact of silencing of AfPXG on maize seed colonization by A. flavus. (A) Maize seeds infected with a wild-type A. flavus strain (left) or strain (+) siRNAPXG1 (right). After sterilization, grains were place in a sterile petri plate and directly inoculated with a 200 μl of a liquid culture of A. flavus in PD broth. The photograph was taken at 7 days after infection. (B) Estimation of the mycelium weight and level of aflatoxin B1 accumulation in the (+) siRNAPXG1 and WT strains on day 7 after infection of maize seeds. Asterisks indicate significant differences between the strains in which AfPXG was silenced and the wild type (**, P < 0.01).
