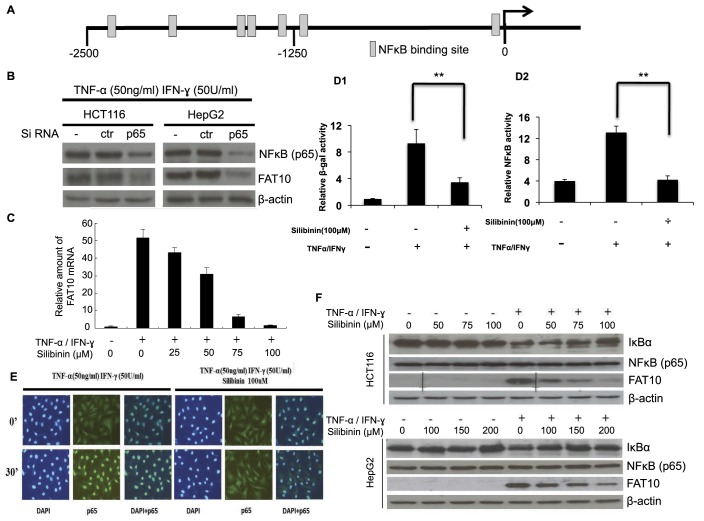
Fig. 3.
Silibinin inhibits TNF-α/IFN-γ (TI)-induced endogenous FAT10 expression through NF-κB signaling pathway. (A) Seven predicted binding sites of NF-κB were found within 2.5 kb upstream of FAT10 promoter region by GenomatixMatInspector Version 8.0 (http://www.genomatix.de). (B) p65 plays a role in modulating FAT10 expression induced by TI. Cells were electroporated with control siRNA (ctr) or siRNAs against p65 (p65) and grown for 24 h. They were then cultured with or without TI for 8 h before harvest. Inhibition of NF-κB subunit p65 expression by its specific siRNA and FAT10 expression were confirmed by western blot. (C) Silibinin inhibits TI-induced FAT10 mRNA levels in a dose dependent manner. Real-time reverse transcription (RT)-PCR was performed to measure the levels of FAT10 mRNA. (D1) Silibinin inhibits TI-induced FAT10 promoter and (D2) Silibinin inhibits NF-κB activities. FAT10-promoter driven β-galactosidase reporter and the NF-κB-SEAP constructs were co-transfected into HepG2 cells using Lipofectamine 2000. 36 h after transfection, cells were treated with TNF-α (50 ng/ml) and IFN-γ (50 U/ml), in the presence or absence of 100 µM silibinin. Nine hours later, cells were harvested and FAT10-promoter driven β-galactosidase reporter and NF-κB driven SEAP activities were determined and normalized against GFP expression and total protein content. All data are shown as mean±s.e. (standard error). **P<0.01 compared to no Silibinin treatment. (E) Silibinin inhibits TI-induced p65 nuclear translocation. Nuclear localization of the p65 subunit of NF-κB in HepG2 cells was detected by immunofluorescence analysis using p65 antibody. (F) Silibinin modulates key molecules of the NF-κB pathway. Western blot analyses were performed to determine the protein expression of FAT10 and NF-κB (p65) in cells treated with TI in the presence or absence of silibinin.