FIG 2.
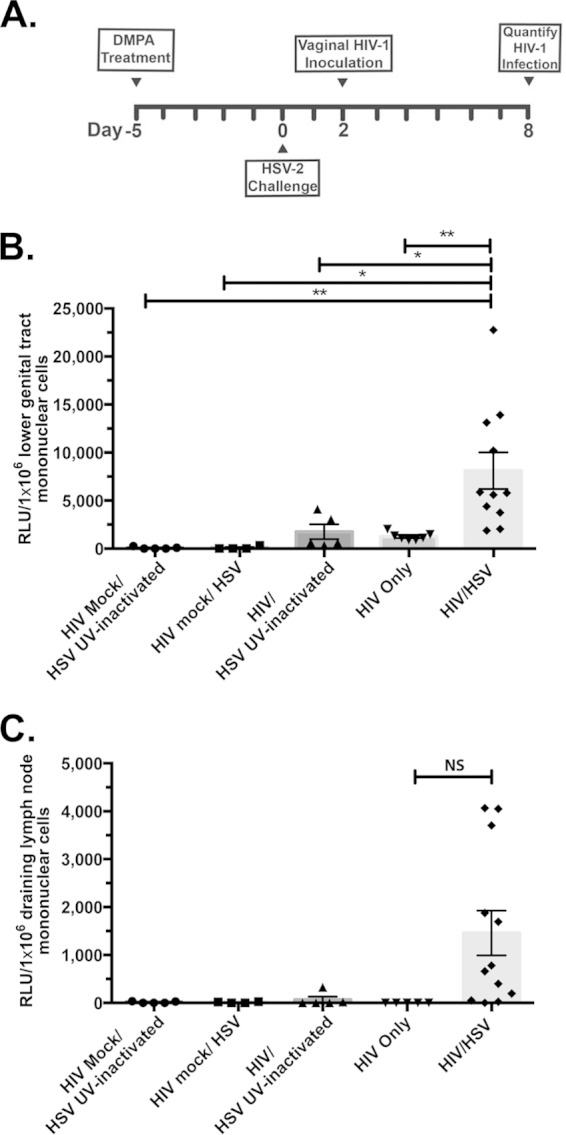
Acute HSV-2 infection increases mucosal HIV-1 infection. hCD4/R5/cT1 mice were intravaginally mock challenged or challenged with infectious HSV-2 or UV-inactivated HSV-2 5 days after subcutaneous injection with DMPA (2.5 mg). Two days after challenge, some mice from each group were then intravaginally mock challenged or challenged with HIV-Du151.2env-NLuc (4.5 × 105 IU). (A) The experimental design. (B) Six days after HIV infection, lower genital tract mononuclear cells were isolated, and NLuc activity in the cellular lysate was quantified. (C) Six days after HIV-1 infection, mononuclear cells were isolated from the draining lymph nodes, and the NLuc activity in the cellular lysate was quantified. The average NLuc activity from two pooled experiments in the cellular lysates from each group ± standard error of the mean and individual data points are shown; values are reported as RLU corresponding to a normalized analysis of 106 mononuclear cells. Asterisks indicate significance using one-way ANOVA with Tukey's test for multiple comparisons (NS, not significant; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01).
