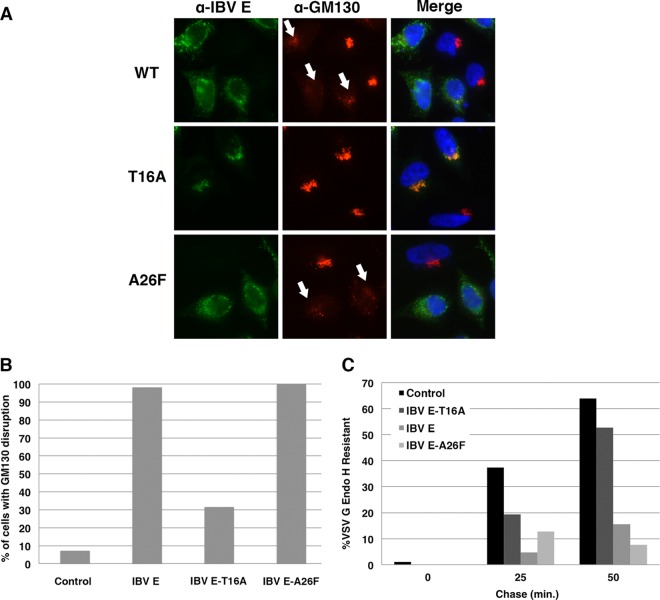
FIG 5.
Predicted HD ion channel mutants of IBV E have different effects on the cellular secretory pathway. (A) HeLa cells expressing IBV E, IBV E-T16A, or IBV E-A26F were analyzed by indirect immunofluorescence microscopy at 16 h posttransfection. Cells were labeled with rabbit anti-IBV E and mouse anti-GM130, a cis-Golgi marker. Secondary antibodies were Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG and Alexa Fluor 568-conjugated anti-mouse IgG. The DNA was stained with Hoechst 33285. White arrows, disrupted Golgi complexes. (B) Quantification of the percentage of cells with Golgi complex disruption (see Materials and Methods). Data are for ≥100 cells for each condition. (C) HeLa cells coexpressing VSV G and IBV E, IBV E-T16A, IBV E-A26F, or IBV M (as a control) were pulse-labeled with [35S]cysteine-methionine for 10 min, and VSV G was immunoprecipitated at the indicated times of chase and digested with endo H. The graph shows the percentage of endo H-resistant VSV G in cells coexpressing each IBV E construct.