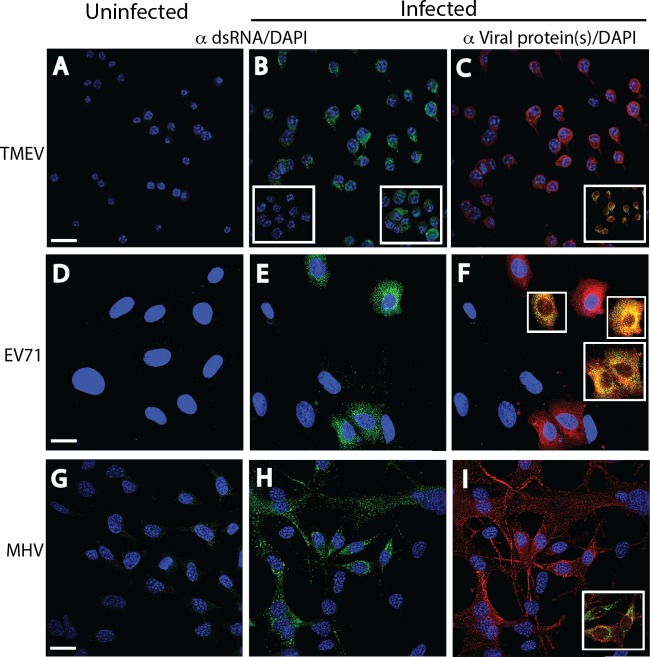
FIG 2.
Immunofluorescence analysis of cell monolayers infected with positive-strand RNA viruses. Uninfected (A, D, G) and infected (B, E, H) cell monolayers were stained with a 1:2,000 dilution of either MAb 9D5 or polyclonal antibody 170A to dsRNA, and infected cells were stained with specific antiviral antibodies (C, F, I). The fields in the center (B, E, H) and right (C, F, I) panels are identical. (A to C) Uninfected and TMEV-infected M1-D macrophages. (A) Uninfected cells. (B) TMEV-infected cells showing strong punctate cytoplasmic staining (green). (Insets) A loss of staining after preincubation with RNase III (left) but retention of staining after preincubation with RNase A (right). (C) TMEV-infected cells stained with a 1:3,000 dilution of rabbit polyclonal antibodies to TMEV virions showing cytoplasmic staining (red). (Inset) Colocalization of dsRNA and virus antigen(s). (D to F) Uninfected and EV71-infected Vero B6 cells. Strong punctate cytoplasmic dsRNA staining (green) was shown in uninfected cells (D) but not in infected cells (E). (F) EV71-infected cells exhibited cytoplasmic staining with a 1:2,000 dilution of mouse MAb to EV71 (red; virus protein specificity is not known). (Insets) Colocalization of both antigens. (G to I) Uninfected and MHV-infected DBT astrocytoma cells. Strong punctate cytoplasmic staining (green) with the 170A polyclonal antibody was shown in infected cells (H) but not in uninfected cells (G), while MHV-infected cells exhibited cytoplasmic staining with a 1:500 dilution of mouse MAb to MHV M protein (red) (I). The inset in panel I shows the colocalization of both antigens. The results of incubations of RNases with EV71 and MHV are the same as those for incubations of RNases with TMEV (not shown). Bars, 10 μm. All insets have the same magnification as the full panels.