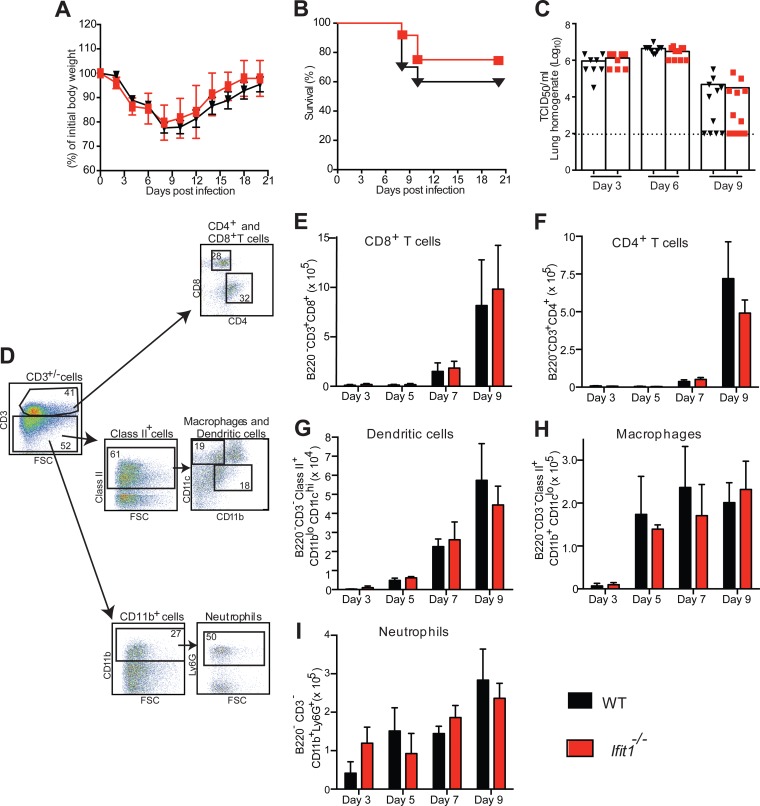
FIG 6.
Murine Ifit1 does not affect virus infection, pathogenesis, or cellular infiltrates in vivo after infection with IAV. (A and B) Morbidity and survival analyses of 6- to 7-week-old female mice after intranasal inoculation of WT (n = 19) and Ifit1−/− mice (n = 10 for morbidity study and n = 19 for mortality study) with 104 EID50 of IAV-Cal. Data were pooled from four independent experiments. (C) Viral burdens in lung homogenates on days 3, 6, and 9 after IAV infection of WT and Ifit1−/− mice were measured by a TCID50 assay on MDCK cells. A scatterplot of the data is shown, with each individual point representing a single animal (n = 8 to 12). The dashed line represents the limit of detection of the assay. Statistical significance was judged by the Mann-Whitney test. (D) Representative flow plots showing the gating strategy for BAL fluid immune cell analysis. (E to I) BAL fluid cell composition in WT and Ifit1−/− mice after infection with IAV-Cal. Three, 5, 7, and 9 days after inoculation with 104 EID50 of IAV-Cal, BAL was performed, and the cellular composition of the fluid was determined by flow cytometry, using monoclonal antibodies against mouse CD3, CD4, CD8, CD11c, CD11b, Ly6G, MHC class II, and B220. The data shown are the numbers of CD8+ T cells (B220− CD3+ CD8+) (E), CD4+ T cells (B220− CD3+ CD4+) (F), dendritic cells (B220− CD3− MHC class II+ CD11blo CD11chi) (G), macrophages (B220− CD3− MHC class II+ CD11b+ CD11clo) (H), and neutrophils (B220− CD3− CD11b+ Ly6G+) (I). The data were pooled from three experiments, each containing at least three WT and Ifit1−/− mice. No statistical differences were observed as judged by the Mann-Whitney test.