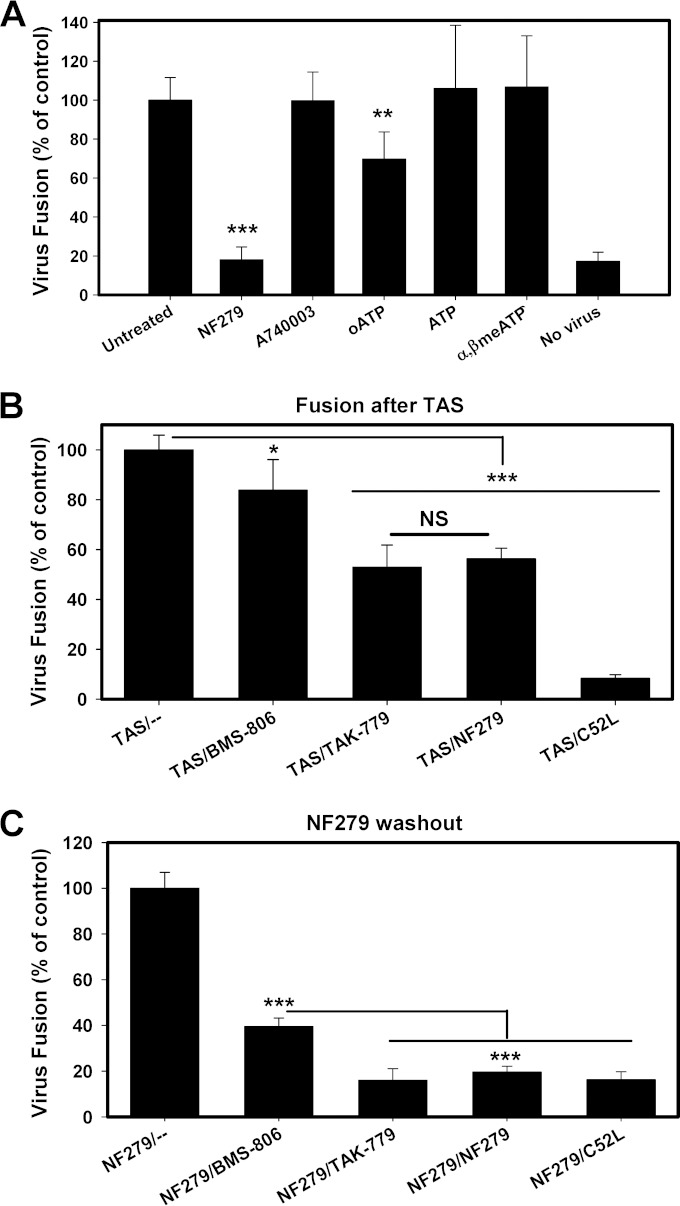
FIG 5.
NF279 inhibits HIV-1–coreceptor engagement in primary human macrophages. (A) Fusion of BaL26pp with MDMs was allowed to proceed in the absence or in the presence of 50 μM NF279 or 100 μM each A740003, ATP, α,β-meATP, and oATP. (B) A TAS of fusion between BaL26pp and MDMs was created, essentially as described in the legends of Fig. 4B and C. BaL26 pseudoviruses were prebound to MDMs and incubated for 2.5 h at a low temperature (18°C), after which time a fully inhibitory concentration of BMS-806, TAK-779, C52L, or NF279 (50 μM) was added. Fusion was then induced by raising the temperature to 37°C. (C) NF279 washout experiments were performed by creating a TAS of fusion between BaL26pp and MDMs in the presence of a fully inhibitory concentration of NF279, as described in the legends of Fig. 4D and E. Before the temperature was raised to allow fusion, NF279 was replaced with fully inhibitory concentrations of HIV-1 fusion inhibitors. Data in panels A to C are the normalized mean BlaM signals and standard deviations from two independent experiments carried out in triplicate. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; NS, not significant.