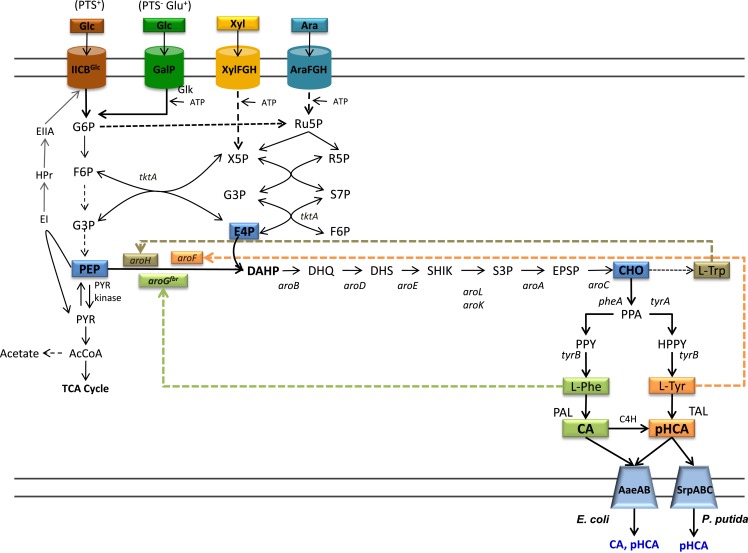
Figure 1.
Central metabolism, aromatics biosynthetic pathways, and transport pathways from engineered E. coli. Dashed arrows indicate multiple enzyme reactions. EI, PTS enzyme I; HPr, PTS phosphohistidine carrier protein; EIIA, PTS glucose-specific enzyme II; PTS IICBGlc, integral membrane glucose permease; GalP, galactose permease; XylFGH, xylose transport proteins, AraFGH, arabinose transport proteins; DAHPS, DAHP synthase; aroGfbr, gene encoding a feedback-inhibition-resistant version of DAHPS; tktA, transketolase; tyrB, tyrosine aminotransferase gene; PAL, phenylalanine ammonia lyase; TAL, tyrosine ammonia lyase; C4H, cinnamate 4-hydroxylase; AaeXAB, efflux pump from E. coli; SprABC, efflux pump from P. putida; G6P, glucose-6-phosphate; F6P, fructose-6-phosphate; G3P, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; R5P, ribose-5-phosphate; Ru5P, ribulose-5-phosphate; S7P, sedoheptulose-7-phosphate; X5P, xylulose-5-phosphate; PYR, pyruvate; AcCoA, acetyl-CoA; TCA, tricarboxylic acids.