Figure 2.
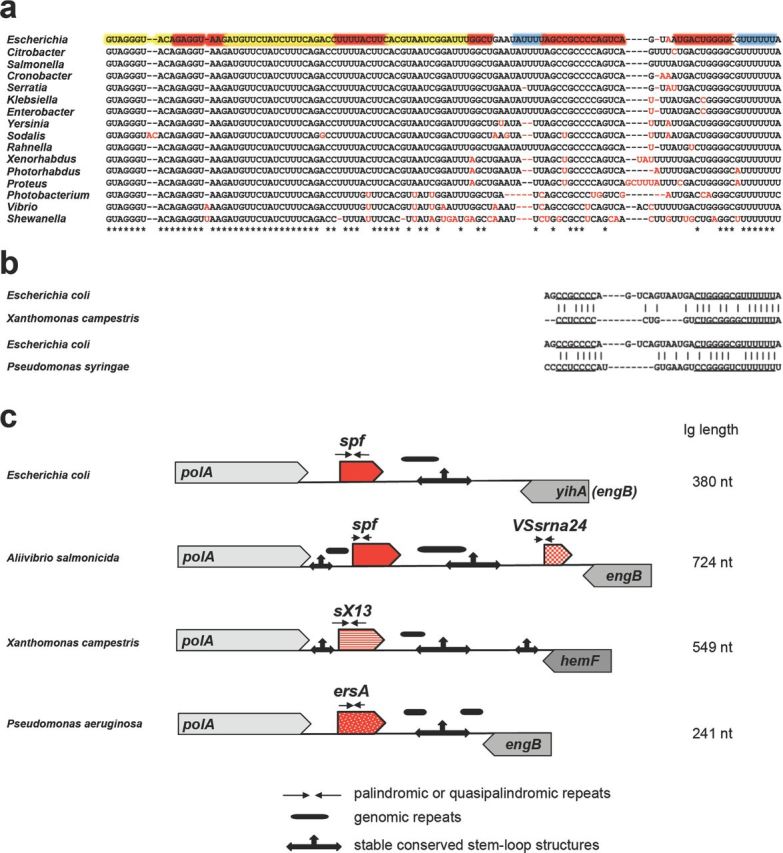
Mechanisms of sRNA evolution illustrated for Spot 42 (encoded by the spf gene), VSsrna24, sX13 and ErsA encoded downstream of polA. Alignment of Spot 42 in Gammaproteobacteria showing the contributions of single nucleotide substitutions and deletions to Spot 42 evolution (a) and similarity of terminators among the sRNAs found downstream of polA in E. coli, Xanthomonas campestris and P. syringae (b). The coloring of the E. coli sequence in (a) is the same as in Fig. 1a. (c) Architecture of the intergenic region (Ig) downstream of polA showing the location of variable repeats and conserved stable hairpins and suggesting the contribution of palindrome misalignment to sRNA evolution. The different sRNA families are indicated by the different patterns of the red arrows. The corresponding trees for the sRNAs found downstream of polA in γ-proteobacteria, Xanthomonadaceae and Pseudomonadaceae are given in Fig. S1 (Supporting Information).
