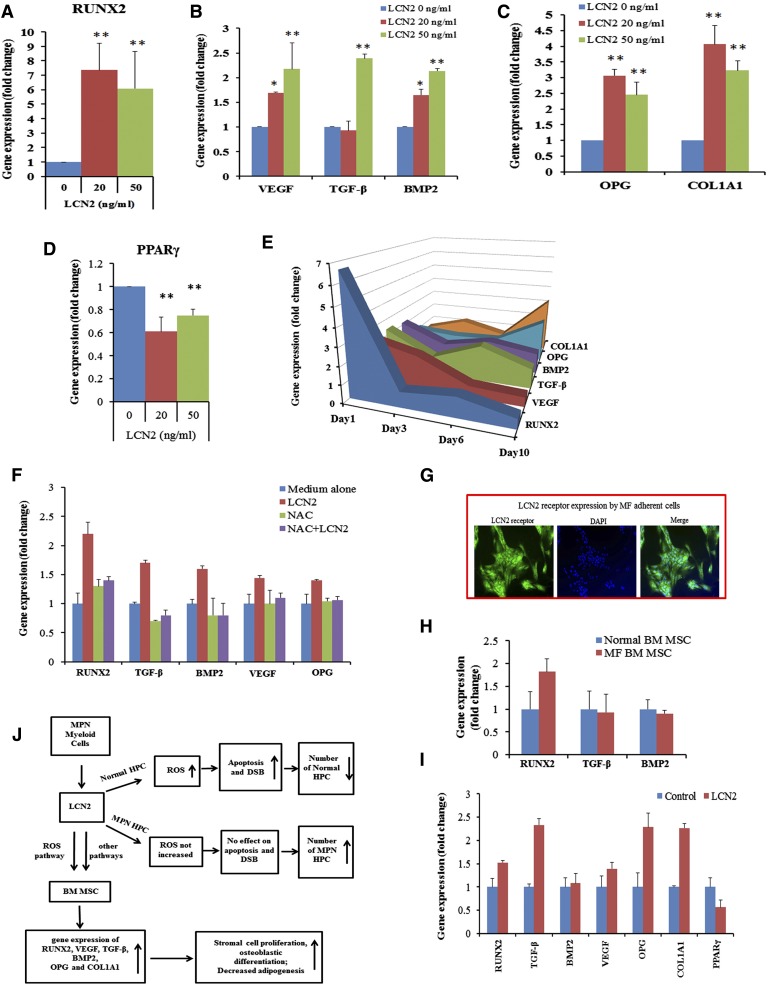
Figure 7.
LCN2 treatment of BM ACs induces expression of genes associated with osteoblastic, but not the adipocytic, differentiation program. qRT-PCR revealed that RUNX2 transcript levels were increased 1 day after incubation with LCN2 (A); VEGF, TGF-β, and BMP2 transcripts were also increased by the addition of LCN2 in a dose-dependent fashion after 1 day (B); LCN2 treatment increased OPG and COL1A1 gene expression after 10 days of incubation (C); and PPARγ gene levels were decreased after 1 day of incubation with LCN2 (D). (E) Three-dimensional area graph showing the time course of expression of various genes by BM ACs after incubation with LCN2 (50 ng/mL). (F) Addition of NAC blocked the expression of RUNX2, VEGF, TGF-β, BMP2, and OPG transcripts induced by LCN2 after 1 day. (G) Immunofluorescence staining with an anti-LCN2 receptor antibody (SLC22A17) revealed that MF BM ACs expressed the LCN2 receptor (green); nuclei were stained with DAPI. (H) qRT-PCR results revealed that RUNX2 transcription levels were increased in untreated MF BM ACs. (I) qRT-PCR showed that 10 days of treatment with LCN2 increased RUNX2, TGF-β, VEGF, and OPG gene expression but decreased PPARγ gene expression by MF BM ACs. (J) Diagram summarizing the proposed effects of LCN2 on hematopoietic progenitor cells and BM stromal cells in MF. DSB, DNA strand break; HPC, hematopoietic progenitor cells.