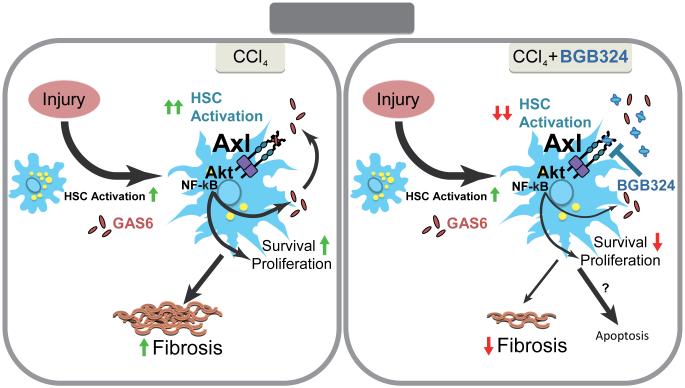
Figure 6. Schematic representation of Gas6/Axl role in liver fibrosis induced by chronic damage.
In a mouse model of chemical-induced liver fibrosis Gas6/Axl signaling is induced. Increased Gas6 extracellular levels stimulate Axl activation in HSCs leading to HSC proliferation and phenotypic transformation via AKT phosphorylation and NF-κB nuclear translocation. Axl genetic deficiency (Axl KO mice) or Axl inhibition by BGB324 blocks fibrogenesis, effectively inhibiting Gas6-induced HSC activation in vitro and reducing experimental liver fibrosis in vivo by eliminating activated HSCs. Therefore, small molecule inhibitors of Axl may be interesting compounds for the medical treatment of chronic liver fibrosis and prevention of HCC development.