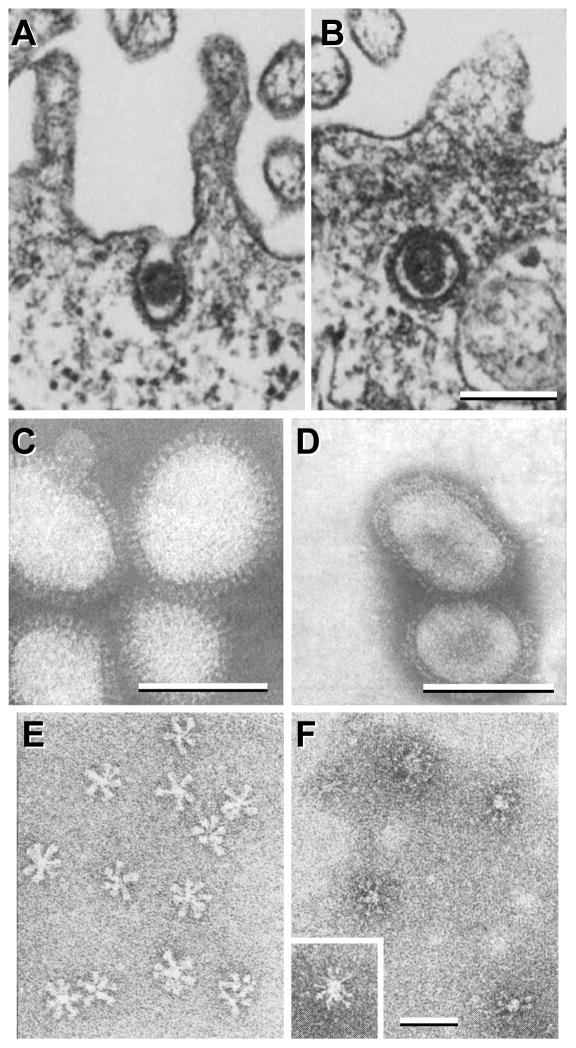
Figure 7. Thin section and negative stain EM of influenza virions and HA rosettes.
A–B, influenza virions entering mammalian cells using clathrin-coated vesicles (fowl plague virus strain). C–F, negative stain EM of influenza virions (C & D) and of HA rosettes (E & F) at neutral (C & E) and low pH (D & F). The X-49 strain (H3N2) was used for C & D, and the X-31 strain (H3N2) was used for E & F. A & B are reprinted from Matlin et al., 1981, Infectious entry pathway of influenza virus in a canine kidney cell line, Journal of Cell Biology 91(3):601–613, with permission from the Journal of Cell Biology [48]; C & D are from Ruigrok et al., 1984, Archives of Virology 82(3):181–194, reprinted with permission from Springer Science and Business Media [50]; E & F are reprinted from Ruigrok et al., 1986, Electron microscopy of the low pH structure of influenza virus haemagglutinin, EMBO Journal 5(1):41–49, with permission from EMBO [52]. Bars, 200 nm for A & B; 50 nm for C–F.