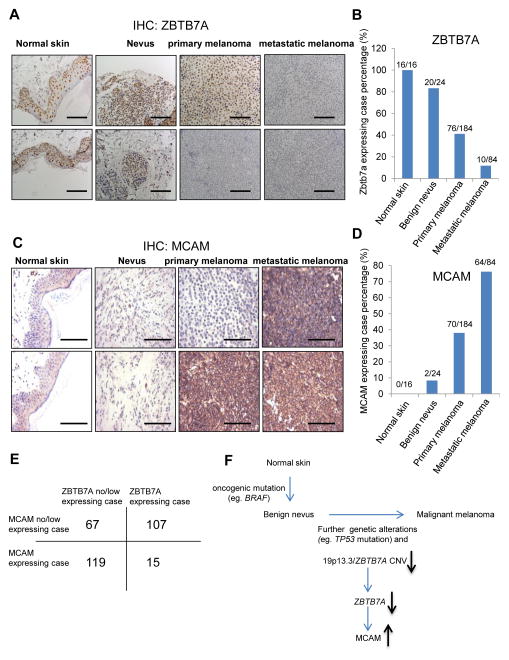
Figure 7.
An inverse correlation between ZBTB7A and MCAM in human melanoma. A, detection of ZBTB7A protein by immunohistochemistry in tissue microarrays of human normal skin, benign nevus, primary and metastatic melanoma samples. Bar, 50μm. B, statistical analysis of ZBTB7A expression levels in normal skin, benign nevus, primary and metastatic melanoma tissues. ZBTB7A is expressed in 100% (16 of 16) normal skin, 83% (20 of 24) benign nevus, 41% (76 of 184) primary melanoma and 12% (10 of 84) metastatic melanoma. C, detection of MCAM protein by immunohistochemistry in tissue microarrays of human normal skin, benign nevus, primary and metastatic melanoma samples. Bar, 50μm. D, statistical analysis of MCAM expression levels in normal skin, benign nevus, primary and metastatic melanoma samples. MCAM is expressed in 0% (0 of 16) normal skin, 8% (2 of 24) benign nevus, 38% (70 of 184) primary melanoma and 76% (64 of 84) metastatic melanoma. E, an inverse-correlation between ZBTB7A and MCAM expression in tissue microarray samples. F, model for the function of ZBTB7A in the regulation of melanoma progression and metastasis.